Overview
A toe fracture is a break or crack in one or more of the bones in the toes, often resulting from trauma, sports injuries, or accidents. While sometimes considered minor compared to other fractures, toe fractures can cause significant pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. In South Korea, orthopedic specialists provide advanced diagnostic imaging, precise treatment plans, and rehabilitation programs to ensure optimal recovery. Korean healthcare emphasizes early diagnosis, proper alignment, and physiotherapy to prevent long-term deformities and restore mobility.
What is a Toe Fracture?
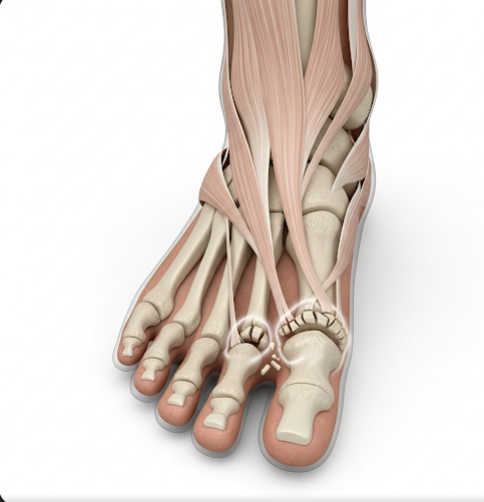
A toe fracture occurs when one of the phalanges or metatarsal bones in the toes is broken. These fractures can range from simple cracks in the bone to complex, displaced breaks. Toe fractures are commonly classified as:
- Distal phalanx fracture: Involving the tip of the toe
- Middle phalanx fracture: Fracture of the central segment
- Proximal phalanx fracture: Closest to the foot, often affecting weight-bearing
- Metatarsal fractures: Involving the long bones connected to the toes
Toe fractures can result from direct trauma, twisting injuries, repetitive stress, or crush injuries. In Korea, orthopedic clinics emphasize accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment to prevent complications such as malunion or chronic pain.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a toe fracture may vary depending on the severity and location but typically include:
- Sudden, sharp pain at the site of injury
- Swelling and bruising around the affected toe
- Difficulty walking or bearing weight
- Deformity or misalignment of the toe
- Tenderness to touch
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion
- In severe cases, open fractures with visible bone protrusion
Prompt recognition of these symptoms is essential to prevent improper healing, especially in athletes or elderly patients.
Causes
Toe fractures usually occur due to trauma or mechanical stress. Common causes include:
- Direct impact from dropping heavy objects on the foot
- Stubbing the toe against furniture or hard surfaces
- Sports injuries involving kicking, twisting, or falling
- Repetitive stress injuries, especially in runners and dancers
- Motor vehicle accidents or crush injuries
- Osteoporosis or weakened bones, making fractures more likely
Korean orthopedic specialists assess the mechanism of injury to determine fracture type and plan the most effective treatment.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of sustaining a toe fracture:
- Participation in high-impact sports or activities
- Poor footwear that offers inadequate protection or support
- Osteoporosis or other bone-weakening conditions
- Age, with elderly individuals more susceptible to falls
- Previous foot injuries that may weaken bone integrity
- Occupational hazards involving heavy lifting or machinery
In South Korea, preventive strategies focus on protective gear, fall prevention, and awareness of risky activities.
Complications
Although toe fractures are often considered minor, untreated or improperly managed fractures can lead to complications:
- Malunion or misalignment of the toe
- Chronic pain or discomfort while walking
- Reduced mobility or flexibility
- Arthritis in the affected joint over time
- Infection, especially in open fractures
- Development of hammer toe or other deformities
Korean orthopedic clinics emphasize proper immobilization, surgical intervention when necessary, and rehabilitation to minimize these risks.
Prevention
Preventing toe fractures involves reducing exposure to trauma and maintaining bone health:
- Wear protective footwear: Especially in sports, construction, or industrial environments
- Home safety: Avoid clutter and use caution on slippery surfaces
- Strength and balance training: Particularly for elderly individuals to prevent falls
- Maintain bone health: Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake
- Avoid repetitive stress: Gradually increase intensity in physical activities and sports
- Immediate care for minor injuries: Early evaluation prevents progression to severe fractures
South Korean public health campaigns often highlight preventive strategies for athletes and high-risk populations.
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment of toe fractures in Korea is guided by fracture type, severity, and patient needs. The approach may be conservative or surgical:
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination and assessment of deformity
- X-rays to confirm fracture location, type, and displacement
- CT scans for complex or multi-fragment fractures
- Assessment of blood flow, nerve function, and soft tissue involvement
Medical Treatments:
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE): To reduce swelling and pain
- Buddy taping: Taping the fractured toe to an adjacent toe for stability
- Splints or orthopedic footwear: To immobilize and protect the toe
- Pain management: NSAIDs or acetaminophen for discomfort
- Surgery: Indicated for severely displaced, open, or multiple fractures, including pinning or fixation
Rehabilitation and Supportive Care:
- Gradual weight-bearing and physical therapy to restore mobility
- Exercises to improve strength and range of motion
- Follow-up imaging to ensure proper healing
- Patient education on avoiding re-injury
Korean orthopedic centers integrate advanced imaging, minimally invasive surgery, and structured physiotherapy programs to ensure complete recovery and prevent long-term complications.