Overview
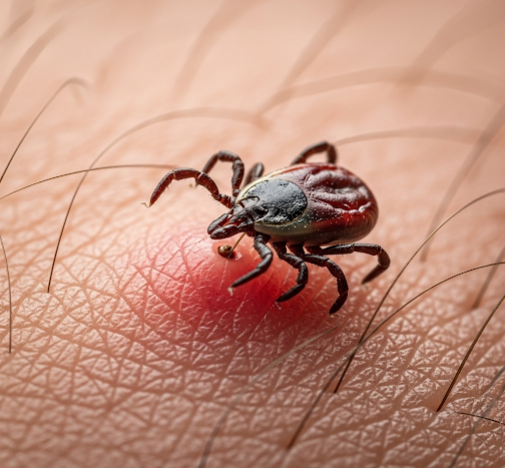
A tick bite occurs when a tick, a small parasitic arachnid, attaches to human skin and feeds on blood. While often painless, tick bites can transmit various infectious diseases, including Lyme disease, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), and rickettsial infections. In Korea, tick-borne illnesses are a growing public health concern, particularly in rural and forested regions. South Korea provides advanced diagnostic facilities, rapid laboratory testing, and effective treatment protocols to manage tick-borne infections and minimize complications. Awareness, early detection, and appropriate medical care are crucial for preventing serious health issues following a tick bite.
What is a Tick Bite?
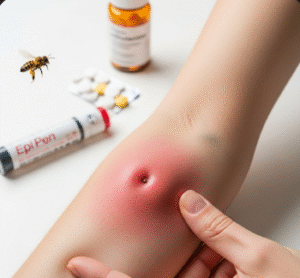
A tick bite occurs when a tick latches onto the skin and inserts its mouthparts to feed on blood. Ticks are commonly found in grassy, wooded, or rural areas and can attach to any part of the body, though they often prefer areas such as the scalp, armpits, groin, and behind the ears. Most tick bites are harmless if removed promptly; however, infected ticks can transmit pathogens that cause serious illnesses. Tick bites can result in local skin reactions, systemic infection, and, in severe cases, multi-organ involvement depending on the pathogen.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a tick bite vary depending on whether the tick transmitted an infectious agent:
Local symptoms:
- Small red bump or papule at the bite site
- Mild itching or irritation
- Swelling or warmth around the bite
- Rash, sometimes forming a “bullseye” pattern (common in Lyme disease)
Systemic symptoms (if infection occurs):
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Fatigue or general malaise
- Muscle or joint pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swollen lymph nodes
Severe or delayed symptoms (in cases of tick-borne disease):
- Neurological issues such as facial palsy or meningitis
- Severe gastrointestinal symptoms
- Hemorrhagic fever and low platelet count (in SFTS)
- Organ dysfunction if left untreated
Causes
Tick bites are caused by the attachment of ticks that feed on human blood. Ticks can carry several pathogens, leading to infectious complications:
- Bacterial infections: Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease), Rickettsia species (rickettsial diseases)
- Viral infections: Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV)
- Protozoan infections: Babesia species, leading to babesiosis
- Environmental exposure: Walking, hiking, or working in grassy, wooded, or rural areas where ticks are present
Ticks become infected by feeding on animals carrying these pathogens and can transmit them to humans during prolonged attachment.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of acquiring tick bites and tick-borne diseases:
- Spending time outdoors in forests, fields, or rural areas
- Handling animals or livestock that may carry ticks
- Walking barefoot or wearing insufficient protective clothing in endemic regions
- Failure to use insect repellents or other preventive measures
- Immunocompromised individuals may be more susceptible to severe infections
Complications
While many tick bites heal without serious consequences, some can lead to complications if the tick transmits pathogens:
- Lyme disease: Can cause arthritis, neurological issues, and cardiac problems if untreated
- Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS): High fever, bleeding tendencies, multi-organ failure, and potentially death
- Rickettsial infections: Fever, rash, and vascular complications
- Secondary skin infections: Bacterial infection at the bite site
- Chronic fatigue or persistent symptoms: Following some tick-borne diseases
Early detection and intervention are critical to preventing these complications.
Prevention
Preventing tick bites and associated diseases involves personal protection, environmental awareness, and prompt action:
- Wear long sleeves, pants, and closed shoes in tick-prone areas
- Use insect repellents containing DEET or permethrin on clothing and skin
- Avoid walking through tall grass or dense underbrush
- Perform thorough tick checks on the body after outdoor activities
- Promptly remove any attached tick using fine-tipped tweezers
- Keep yards and outdoor spaces well-maintained to reduce tick habitats
- Vaccination is not currently available for most tick-borne diseases, making preventive behavior essential
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides specialized medical care for tick bites, focusing on rapid removal, diagnosis, and treatment of potential infections.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical evaluation of the bite site and history of exposure
- Blood tests to detect infections such as Lyme disease, SFTS, and rickettsial diseases
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for pathogen identification
- Complete blood count and liver function tests for systemic involvement
Medical Treatments:
- Immediate tick removal: Using proper technique to reduce the risk of infection
- Antibiotics: Doxycycline or other appropriate antibiotics for bacterial tick-borne infections
- Supportive care: Intravenous fluids, fever management, and symptom relief for viral infections
- Hospitalization: Required for severe cases such as SFTS or systemic rickettsial infections
Rehabilitation and Support:
- Follow-up laboratory tests to monitor treatment efficacy
- Management of chronic symptoms or complications
- Education on tick avoidance and preventive strategies for future exposure
- Counseling for patients experiencing prolonged fatigue or neurological effects
South Korea’s healthcare system emphasizes early intervention, accurate diagnosis, and multidisciplinary management to ensure patients recover fully from tick bites and any associated infections.