Overview
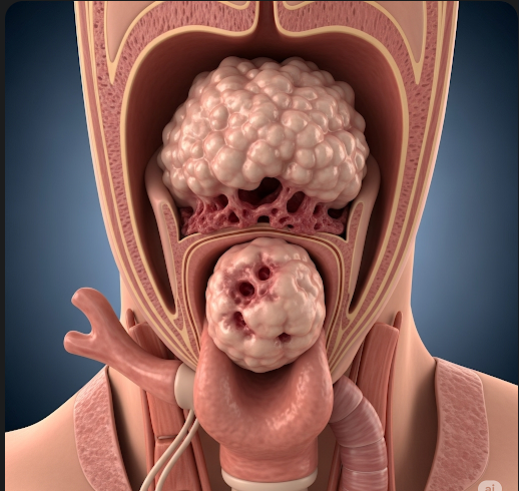
Throat cancer refers to malignant tumors that develop in the pharynx, larynx, or other areas of the throat. This type of cancer can affect voice, swallowing, breathing, and overall quality of life. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. South Korea offers advanced diagnostic facilities, precision radiotherapy, minimally invasive surgery, and comprehensive oncology care, providing patients with modern, effective treatment options and long-term follow-up care.
What is Throat Cancer?
Throat cancer is a general term for cancers that arise in the throat region, including:
- Pharyngeal cancer: Cancer in the pharynx, which is the hollow tube connecting the nasal cavity and mouth to the esophagus.
- Laryngeal cancer: Cancer affecting the larynx or voice box, impacting speech and breathing.
- Hypopharyngeal cancer: Cancer in the lower part of the pharynx near the esophagus.
Most throat cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, originating from the thin, flat cells lining the throat. These cancers can invade nearby tissues and lymph nodes, making early diagnosis and treatment critical.
Symptoms
Symptoms of throat cancer may vary depending on the tumor location and stage:
- Persistent sore throat or cough
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or painful swallowing
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Lump or mass in the neck or throat
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue
- Coughing up blood in advanced cases
- Persistent bad breath or oral odor
Early-stage throat cancer may be asymptomatic or present with subtle symptoms, which is why regular check-ups are essential, especially for high-risk individuals.
Causes
Throat cancer is caused by genetic mutations in the cells lining the throat, leading to uncontrolled cell growth. Risk factors and causative elements include:
- Tobacco use: Cigarette smoking, cigars, or chewing tobacco significantly increase risk.
- Alcohol consumption: Chronic heavy drinking amplifies the risk, especially when combined with smoking.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Certain HPV strains are linked to throat cancers.
- Poor oral hygiene and chronic irritation: Dental infections or chronic inflammation may contribute.
- Exposure to carcinogens: Workplace exposure to chemicals, asbestos, or dust increases susceptibility.
Risk Factors
Individuals with the following risk factors are more likely to develop throat cancer:
- Age over 50 years
- Male gender (higher incidence in men)
- Family history of head and neck cancers
- Chronic smoking and alcohol consumption
- HPV infection
- Occupational exposure to chemicals or industrial pollutants
Complications
If left untreated, throat cancer can lead to severe complications:
- Difficulty swallowing or choking
- Airway obstruction, leading to breathing difficulties
- Spread (metastasis) to lymph nodes, lungs, liver, or bones
- Chronic pain and persistent cough
- Weight loss and malnutrition
- Vocal cord dysfunction or permanent voice loss
- Secondary infections due to immune compromise
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on reducing exposure to risk factors and promoting early detection:
- Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol consumption
- Practice safe sexual behaviors to reduce HPV infection
- Maintain oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups
- Wear protective equipment in workplaces with chemical exposure
- Routine medical examinations and early screening for high-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean medical centers provide state-of-the-art treatment for throat cancer, tailored to tumor stage and patient condition:
1. Surgical Treatments
- Endoscopic surgery: Minimally invasive removal of early-stage tumors
- Partial or total laryngectomy: Removal of part or all of the larynx in advanced cases
- Neck dissection: Removal of affected lymph nodes if cancer has spread
2. Radiation Therapy
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT): Targeted high-energy rays destroy cancer cells
- Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): Precise targeting to minimize damage to healthy tissues
- Brachytherapy: Placement of radioactive material near the tumor for localized treatment
3. Chemotherapy
- Often combined with radiation therapy for advanced or recurrent cancer
- Drugs like cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, or paclitaxel may be used to shrink tumors
4. Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
- Monoclonal antibodies and immunotherapy drugs enhance the body’s immune response against cancer cells
- Used in cases resistant to standard treatment or metastatic disease
5. Supportive Care and Rehabilitation
- Speech therapy for vocal recovery
- Nutritional support for maintaining weight and strength
- Pain management and palliative care when needed
6. Cost and Hospital Care
Treatment costs in Korea vary depending on the complexity and duration of therapy. Leading oncology centers provide multidisciplinary care, including diagnosis, surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and rehabilitation. Early detection combined with modern treatments significantly improves survival rates and quality of life for patients with throat cancer.
With timely diagnosis, precise treatment, and structured rehabilitation, patients with throat cancer in Korea can achieve effective tumor control, preserve function, and improve long-term health outcomes.