Overview
Tattooing is a popular form of body art and self-expression that involves injecting ink into the skin. While generally safe when performed under hygienic conditions, tattooing carries the risk of infection if proper sterilization and aftercare are not followed. Tattoo infections can range from mild localized skin irritation to severe systemic infections, sometimes requiring urgent medical treatment. In South Korea, where tattoo culture has been growing, strict regulations and professional studios emphasize safety, and the country’s advanced healthcare system offers prompt diagnosis and treatment for tattoo-related infections.
What is Tattoo Infection?
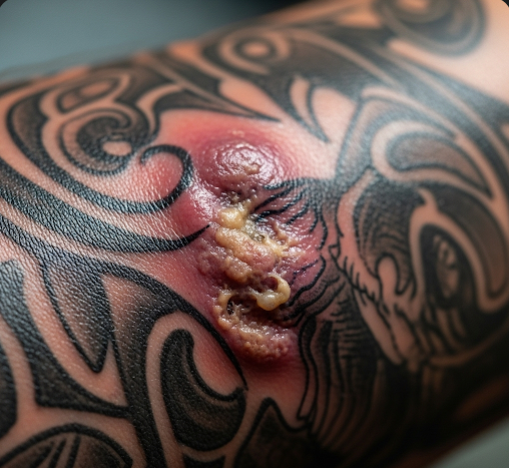
Tattoo infection occurs when harmful microorganisms—bacteria, viruses, or fungi—enter the skin during or after the tattooing process. The skin’s barrier is breached during tattooing, providing a pathway for pathogens if the tattoo equipment, inks, or environment are contaminated, or if aftercare instructions are neglected. Infections can be acute or chronic, and in some cases, complications such as abscess formation or systemic spread can occur.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a tattoo infection include:
- Redness and swelling around the tattoo site
- Warmth and tenderness in the area
- Pain that worsens over time
- Pus or discharge, sometimes with a foul odor
- Fever and chills in more severe infections
- Itching and rash
- Delayed healing or spreading redness indicating cellulitis
Causes
Common causes of tattoo infection include:
- Use of non-sterile needles or equipment
- Contaminated tattoo inks
- Poor hygiene during the tattooing process
- Inadequate aftercare, such as failing to keep the area clean or scratching the tattoo
- Exposure to contaminated water, such as swimming pools or hot tubs before healing
- Pre-existing skin conditions or immune system weaknesses
Risk Factors
- Getting tattooed in unregulated or unlicensed studios
- Compromised immune system due to illness or medications
- Diabetes or other chronic diseases affecting healing
- Poor personal hygiene during and after tattooing
- Using expired or contaminated tattoo inks
- Not following professional aftercare guidelines
Complications
If untreated, tattoo infections can cause:
- Abscesses requiring drainage
- Cellulitis spreading to surrounding skin
- Bloodstream infections (sepsis) in severe cases
- Scarring and permanent skin discoloration
- Allergic reactions complicating infection
- Transmission of bloodborne diseases if equipment is contaminated (e.g., hepatitis B or C, HIV)
Prevention
Preventing tattoo infections involves both tattoo artist and client responsibility:
- Ensure tattooing is performed in licensed, hygienic studios following strict sterilization protocols
- Use of single-use, sterile needles and disposable gloves
- Tattoo inks should be sterile and approved for use
- Follow all aftercare instructions provided by the tattoo artist
- Keep the tattoo clean and dry during healing
- Avoid swimming, hot tubs, and excessive sweating until fully healed
- Avoid picking or scratching the tattooed area
- Seek prompt medical advice if signs of infection appear
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea’s healthcare system provides expert management of tattoo infections through accurate diagnosis and effective treatment:
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination of the affected area
- Swab and culture tests to identify causative microorganisms
- Blood tests in systemic infections
- Imaging in rare cases to assess deeper involvement
Medical Treatment
- Antibiotics targeted at bacterial infections, typically oral but intravenous for severe cases
- Antifungal or antiviral medications if non-bacterial infections are diagnosed
- Pain management and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Wound care including cleaning, dressing, and sometimes surgical drainage of abscesses
Supportive Care
- Education on wound hygiene and proper care during healing
- Monitoring for signs of spreading infection or complications
- Referral to dermatologists or infectious disease specialists as needed
Top Hospitals and Clinics in Korea for Skin Infections
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Asan Medical Center
- Samsung Medical Center
- Specialized dermatology clinics across major cities