Overview
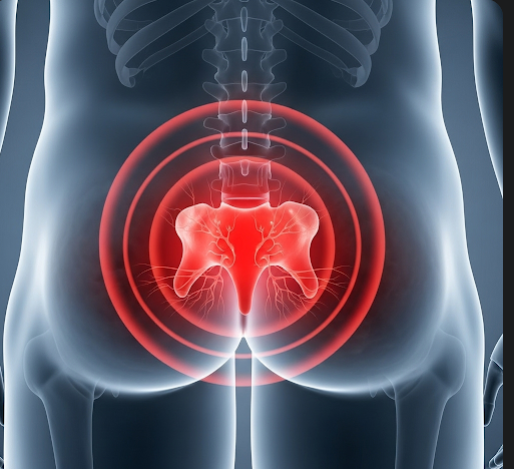
Tailbone pain, medically referred to as coccydynia, is discomfort localized at the coccyx—the small triangular bone at the base of the spine. This condition can result from trauma, prolonged sitting, or degenerative changes, and it may significantly affect daily activities such as sitting, standing, or exercising. In South Korea, patients have access to advanced diagnostic imaging, pain management clinics, physical therapy, and minimally invasive surgical options, ensuring comprehensive care for both acute and chronic tailbone pain.
What is Tailbone (Coccyx) Pain?
Tailbone pain, or coccydynia, is characterized by localized pain at the coccyx, often exacerbated by pressure or movement. The pain can be acute, resulting from a recent injury, or chronic, persisting for weeks to months. It may radiate to surrounding areas, including the lower back, hips, or pelvic region. Tailbone pain is classified based on etiology:
- Traumatic coccydynia: Caused by falls, direct blows, or repetitive stress
- Idiopathic coccydynia: Pain without a clear underlying cause, possibly linked to joint hypermobility or postural factors
- Secondary coccydynia: Related to infections, tumors, or inflammatory conditions
South Korean orthopedic and pain clinics employ a multidisciplinary approach to accurately identify the type and cause of coccyx pain.
Symptoms
Symptoms of tailbone pain vary based on severity and underlying cause, and often include:
- Pain localized at the tip of the coccyx, worsened by sitting or rising from a seated position
- Tenderness to touch at the base of the spine
- Discomfort during bowel movements or sexual activity
- Pain that may radiate to the lower back, hips, or pelvic region
- Stiffness or limited movement in the lower spine
- Swelling or bruising if associated with trauma
Patients may find temporary relief by using cushioned seating or leaning forward while sitting. Chronic symptoms can interfere with work, exercise, and quality of life.
Causes
Tailbone pain can arise from multiple factors affecting the coccyx or surrounding structures:
- Trauma: Falls onto the buttocks, sports injuries, or childbirth-related stress
- Repetitive stress: Cycling, rowing, or prolonged sitting on hard surfaces
- Degenerative changes: Arthritis or age-related wear affecting coccygeal joints
- Postural issues: Poor posture leading to increased pressure on the coccyx
- Infections or tumors: Rare but possible causes requiring thorough evaluation
- Idiopathic factors: Unknown causes that may involve ligament or nerve irritation
South Korean clinicians use patient history, physical examination, and imaging such as X-ray or MRI to identify the underlying cause accurately.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing coccyx pain:
- Female gender, due to wider pelvis and hormonal effects on ligaments
- History of trauma or falls onto the buttocks
- Prolonged sitting on hard surfaces, particularly in sedentary jobs
- Poor posture or ergonomic setup while sitting
- Obesity, increasing pressure on the coccyx
- Childbirth, which can strain or dislocate the coccyx
Preventive education on posture, ergonomics, and protective techniques is emphasized in South Korean pain clinics.
Complications
If left untreated, tailbone pain can lead to chronic discomfort and functional limitations:
- Persistent or worsening pain affecting daily activities
- Reduced mobility or avoidance of sitting for prolonged periods
- Psychological impact, including stress, anxiety, or depression
- Development of secondary musculoskeletal issues due to altered posture
- Chronic inflammation or coccygeal joint instability
- Rarely, infection or abscess formation in severe cases
Early intervention in South Korea prevents chronic complications and promotes faster recovery.
Prevention
Preventing tailbone pain involves lifestyle modifications, ergonomic adjustments, and protective measures:
- Ergonomic seating: Cushioned chairs or specialized tailbone cushions to reduce pressure
- Posture training: Maintaining upright posture and avoiding slouching while sitting
- Activity modification: Reducing prolonged sitting and taking regular breaks
- Protective measures: Padding during sports or activities with fall risk
- Weight management: Reducing excess pressure on the coccyx
- Strengthening exercises: Core and pelvic floor exercises to support spinal alignment
Korean physical therapists often design individualized preventive programs for patients at risk of coccyx pain.
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for tailbone pain in South Korea is comprehensive, ranging from conservative management to surgical intervention in severe cases:
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination to assess tenderness, range of motion, and posture
- Imaging studies, including X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, to detect fractures, dislocations, or degenerative changes
- Evaluation for secondary causes such as infections or tumors
Conservative Treatments:
- Pain management: NSAIDs, topical analgesics, or short-term oral medications
- Cushioning and ergonomic adjustments: Specially designed coccyx cushions or wedge-shaped seats
- Activity modification: Limiting prolonged sitting and avoiding aggravating activities
- Physical therapy: Stretching, strengthening, and postural training to relieve pressure and improve mobility
- Local injections: Corticosteroid or anesthetic injections to reduce inflammation and pain
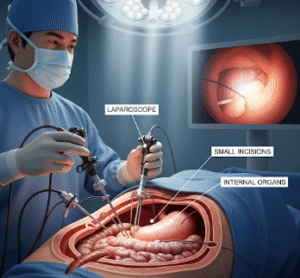
Surgical Treatments:
- Coccygectomy: Surgical removal of the coccyx in cases of chronic, severe pain unresponsive to conservative therapy
- Minimally invasive procedures: Reserved for selected patients with structural abnormalities or persistent joint instability
Supportive Care:
- Education on proper posture, sitting techniques, and daily activity modification
- Pain coping strategies and lifestyle adjustments
- Multidisciplinary follow-up with orthopedic specialists, physical therapists, and pain management teams
South Korean hospitals and pain clinics provide tailored care for coccyx pain, combining medical treatment, rehabilitation, and patient education to optimize recovery and long-term outcomes.