Overview
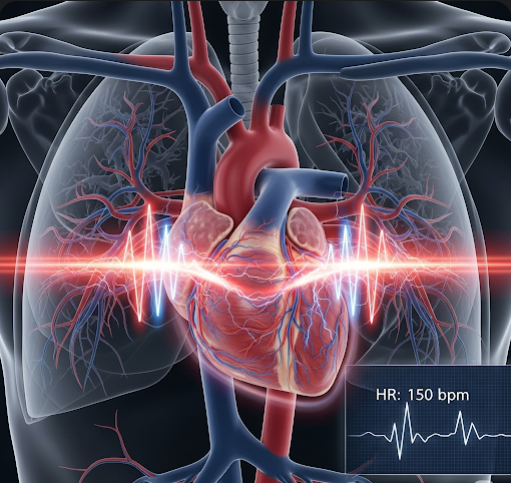
Tachycardia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate, typically defined as a resting heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute in adults. It can be a normal physiological response to stress, exercise, or excitement but may also indicate an underlying health issue requiring medical attention. Tachycardia can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently, potentially leading to complications such as dizziness, fainting, or even heart failure. South Korea, with its advanced cardiovascular healthcare system and expert cardiologists, offers a comprehensive range of diagnostic and treatment services for tachycardia.
What is Tachycardia?
Tachycardia occurs when the electrical impulses in the heart that coordinate heartbeat become irregular or too rapid, causing the heart to beat faster than normal. It is classified into different types depending on its origin within the heart, including atrial tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and supraventricular tachycardia. The condition can be temporary or chronic and may be harmless or life-threatening, depending on the type and underlying causes.
Symptoms
Tachycardia may present with various symptoms, including:
- Palpitations or feeling that the heart is racing or pounding
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fainting or near-fainting spells (syncope)
- Anxiety or a sense of impending doom
Some patients may be asymptomatic and discover tachycardia during routine medical examinations.
Causes
Causes of tachycardia vary widely and may include:
- Heart-related conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, or cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmias caused by abnormal electrical pathways
- Electrolyte imbalances (e.g., potassium or magnesium deficiencies)
- Excessive caffeine, nicotine, or alcohol intake
- Fever or infections
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland)
- Anemia
- Stress, anxiety, or panic attacks
- Use of certain medications or recreational drugs
- Structural abnormalities of the heart
Risk Factors
Risk factors for tachycardia include:
- Existing heart disease or structural heart abnormalities
- High blood pressure
- Excessive consumption of stimulants such as caffeine or energy drinks
- Smoking and alcohol abuse
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Thyroid disorders
- Family history of arrhythmias or sudden cardiac death
- Stress and mental health conditions
- Advanced age
Complications
Untreated or severe tachycardia can lead to complications such as:
- Reduced cardiac output leading to organ damage
- Heart failure due to prolonged rapid heart rate
- Stroke caused by blood clots formed in the heart
- Sudden cardiac arrest or death in malignant forms of tachycardia
- Worsening of underlying heart conditions
Prevention
Preventive measures to reduce the risk of tachycardia include:
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and balanced diet
- Avoiding excessive intake of caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques and counseling
- Controlling underlying medical conditions such as hypertension and thyroid disorders
- Regular health screenings and early treatment of heart diseases
- Avoiding illicit drug use and monitoring prescribed medications
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers comprehensive care for tachycardia, involving advanced diagnostic tools and a spectrum of treatments:
Diagnosis
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to record heart rhythm
- Holter monitor for continuous heart rate tracking over 24-48 hours
- Echocardiography to assess heart structure and function
- Blood tests for thyroid function and electrolyte levels
- Electrophysiological studies to pinpoint abnormal electrical pathways
Treatment
- Medications: Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics to control heart rate and rhythm
- Lifestyle modifications: Reducing stimulant intake, stress management
- Catheter ablation: A minimally invasive procedure to destroy abnormal heart tissue causing arrhythmia
- Implantable devices: Pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) for serious cases
- Surgery: Reserved for complex cases unresponsive to other treatments
Follow-up and Support
- Regular cardiology consultations and monitoring
- Patient education on symptom recognition and lifestyle changes
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs
Top Medical Centers in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital
- Asan Medical Center
- Samsung Medical Center
- Severance Hospital (Yonsei University Health System)
These centers provide cutting-edge cardiology care, including electrophysiology labs and experienced specialists managing tachycardia effectively.