Overview
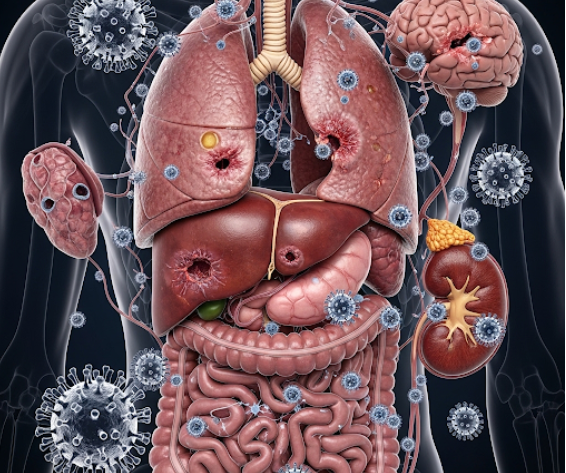
Systemic viral infections occur when a virus spreads throughout the body, affecting multiple organs or systems. Unlike localized viral infections (like the common cold), systemic infections can cause widespread symptoms and complications. These infections can be acute or chronic and require timely diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious health issues.
What is Systemic Viral Infection?
A systemic viral infection means the virus has entered the bloodstream or lymphatic system, enabling it to reach various tissues and organs. Examples include viruses like HIV, hepatitis viruses, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). The infection affects the body beyond the initial site, leading to generalized symptoms and potentially long-term health consequences.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary widely depending on the virus but often include:
- Fever
- Fatigue and weakness
- Muscle and joint pain
- Rash
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Headache
- Sore throat
- Organ-specific symptoms (e.g., jaundice in hepatitis)
- Weight loss in chronic infections
Causes
Systemic viral infections are caused by viruses that can disseminate through blood or lymph, such as:
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Hepatitis B and C viruses
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Measles virus
- Dengue virus
- Influenza virus (severe cases)
Risk Factors
- Immunosuppression (e.g., HIV, cancer chemotherapy)
- Exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids
- Travel to endemic areas
- Unprotected sexual contact
- Use of contaminated needles or medical equipment
- Preexisting chronic diseases
- Poor hygiene and sanitation
Complications
- Chronic infection leading to organ damage (e.g., liver cirrhosis in hepatitis)
- Immune system dysfunction
- Secondary bacterial infections
- Neurological complications (e.g., encephalitis)
- Multi-organ failure in severe cases
- Increased risk of cancers (e.g., lymphoma with EBV)
Prevention
- Vaccinations (e.g., hepatitis B, measles, influenza)
- Safe sex practices and use of barrier protection
- Avoid sharing needles or personal items
- Blood screening for transfusions
- Good hygiene and sanitation practices
- Regular health check-ups and early treatment of viral infections
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced diagnostic and treatment services for systemic viral infections:
- Comprehensive viral testing including PCR, serology, and antigen detection at leading labs
- Antiviral therapies for HIV, hepatitis, CMV, and other systemic viruses
- Supportive care for symptom management
- Immunomodulatory treatments for complications
- Specialized infectious disease centers in major hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital and Samsung Medical Center
- Access to clinical trials and emerging therapies for difficult-to-treat viral infections
- Preventive programs including vaccination drives and public health education