Overview
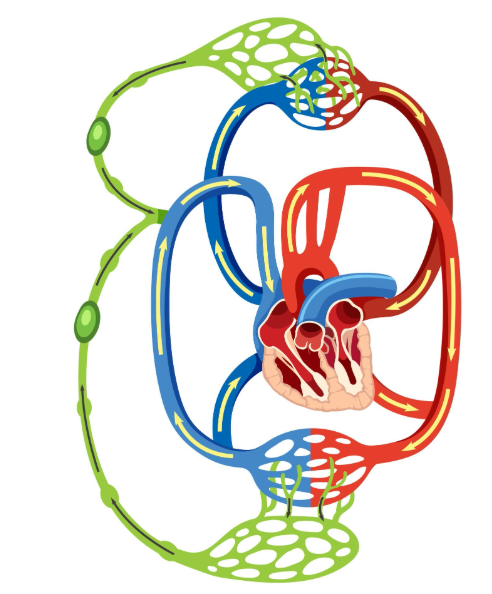
Systemic ischemia is a serious medical condition characterized by reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery to multiple organs and tissues throughout the body. This widespread inadequate perfusion can lead to tissue damage, organ dysfunction, and if untreated, can be life-threatening. Early diagnosis and intervention are vital to prevent complications.
What is Systemic Ischemia?
Systemic ischemia occurs when there is a significant decrease in blood flow that affects various parts of the body, often due to cardiovascular or circulatory system problems. Unlike localized ischemia which affects a specific organ or area, systemic ischemia involves multiple systems simultaneously, compromising overall organ function.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the organs affected but may include:
- Generalized weakness and fatigue
- Confusion or altered mental status
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Cold, pale, or cyanotic skin
- Decreased urine output
- Dizziness or fainting
Causes
- Severe heart failure or cardiogenic shock
- Massive blood loss or hypovolemia
- Severe infections causing septic shock
- Blood clots or embolism blocking major arteries
- Severe anemia reducing oxygen delivery
- Vascular diseases like atherosclerosis
Risk Factors
- History of cardiovascular diseases
- Advanced age
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Chronic kidney disease
Complications
- Multi-organ failure
- Permanent tissue damage or necrosis
- Stroke or heart attack
- Death if untreated promptly
Prevention
- Manage underlying cardiovascular risk factors
- Maintain healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Avoid smoking and maintain healthy weight
- Prompt treatment of infections and acute illnesses
- Regular medical check-ups for high-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced critical care and cardiovascular treatment for systemic ischemia:
- Emergency Management
- Stabilization of airway, breathing, and circulation
- Oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids
- Medications to support heart function and blood pressure
- Diagnostic Evaluation
- Blood tests including lactate levels to assess tissue oxygenation
- Imaging such as echocardiography, CT angiography to identify ischemic areas
- Interventional Procedures
- Cardiac catheterization and angioplasty for coronary artery blockages
- Thrombectomy or thrombolytic therapy to remove clots
- Supportive Care
- Intensive care unit monitoring
- Organ support such as dialysis or mechanical ventilation if needed
- Rehabilitation and Follow-Up
- Cardiovascular rehabilitation programs
- Lifestyle counseling and medications to prevent recurrence