Overview
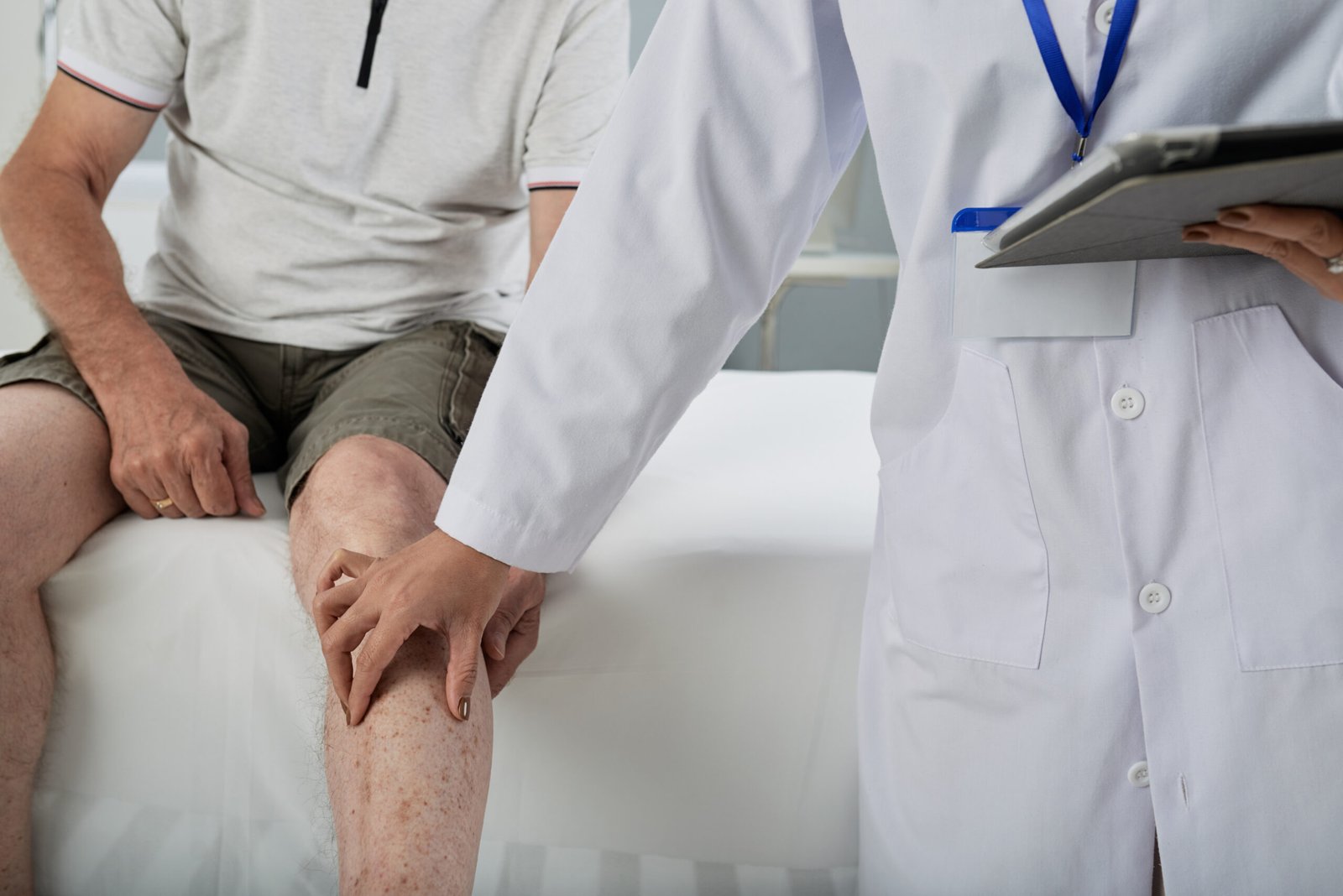
Synovial inflammation refers to the swelling and irritation of the synovial membrane, which lines the joints. This membrane produces synovial fluid that lubricates and nourishes cartilage. Inflammation can result from injury, overuse, autoimmune disorders, or infection, leading to pain, stiffness, and restricted movement. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent chronic joint damage.
What is Synovial Inflammation?
Synovial inflammation, also called synovitis, occurs when the synovial membrane becomes irritated and swollen. This can be a temporary condition due to acute injury or part of a long-term joint disease such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. It often presents with visible swelling, warmth, and tenderness over the affected joint.
Symptoms
- Joint pain and tenderness
- Swelling and puffiness around the joint
- Warmth over the affected area
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after inactivity
- Limited range of motion
Causes
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
- Joint injury or repetitive strain
- Infection in the joint (septic arthritis)
- Crystal deposition (e.g., gout, pseudogout)
- Osteoarthritis progression
Risk Factors
- Family history of autoimmune conditions
- Previous joint injuries
- Aging
- High-impact sports or repetitive joint stress
- Weak immune system (higher risk of infection-related synovitis)
Complications
- Chronic joint pain and stiffness
- Joint deformity
- Cartilage damage leading to osteoarthritis
- Reduced mobility and function
- Spread of infection in septic cases
Prevention
- Protect joints from injury with proper technique and equipment
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Regular low-impact exercise to strengthen muscles
- Prompt treatment of infections and joint injuries
- Manage autoimmune conditions with medical supervision
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, synovial inflammation is treated using advanced diagnostic tools like MRI, ultrasound, and arthroscopy to pinpoint inflammation. Common treatment approaches include:
- Medications: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for autoimmune causes
- Joint aspiration: To remove excess fluid and reduce swelling
- Intra-articular injections: Corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid for inflammation control
- Physical therapy: To improve flexibility and joint function
- Minimally invasive surgery: Arthroscopic synovectomy in severe or chronic cases
Korean hospitals integrate traditional Korean medicine (herbal remedies, acupuncture) alongside modern orthopedics for comprehensive joint care.