Overview
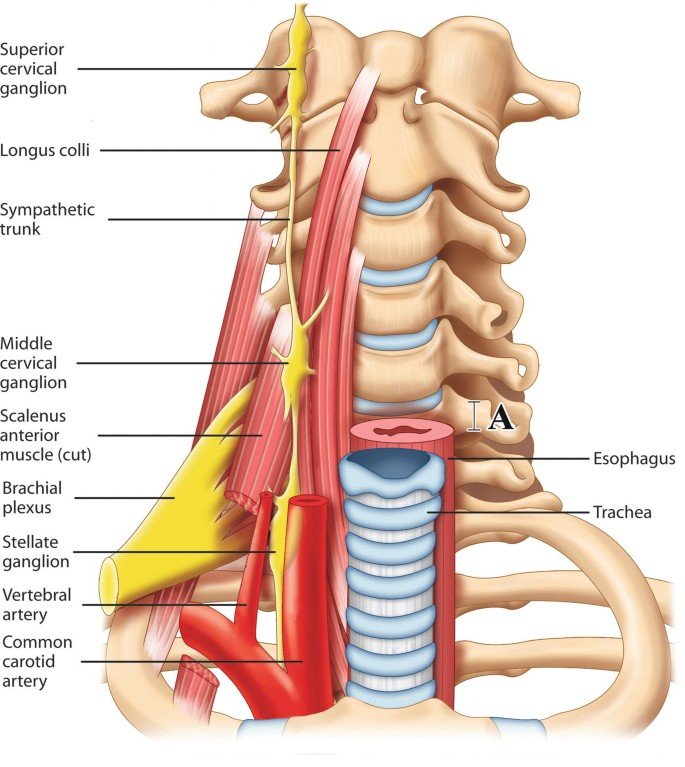
Sympathetic chain injury refers to damage to the sympathetic trunk, a network of nerves that runs alongside the spine and controls involuntary body functions such as pupil dilation, sweating, and blood vessel constriction. Injury to this chain can cause a variety of symptoms, often related to autonomic dysfunction.
What is Sympathetic Chain Injury?
The sympathetic chain is part of the autonomic nervous system and plays a key role in regulating involuntary body responses. Injury can result from trauma, surgery, tumors, or diseases affecting the neck or thoracic region. This injury may lead to disorders such as Horner’s syndrome or autonomic dysfunction.
Symptoms
- Ptosis (drooping eyelid)
- Miosis (constricted pupil)
- Anhidrosis (absence of sweating) on the affected side of the face
- Flushing or skin color changes
- Difficulty regulating blood pressure or heart rate
- Chronic pain or numbness in the affected area
Causes
- Trauma or surgical injury to the neck, chest, or spine
- Tumors compressing the sympathetic chain
- Infections or inflammation affecting nerve tissues
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Spinal cord injuries
Risk Factors
- Neck or chest surgery (e.g., thyroidectomy, lung surgery)
- Trauma such as car accidents or falls
- Tumors in the neck or upper chest region
- Chronic inflammatory diseases
- History of spinal injuries
Complications
- Persistent autonomic dysfunction
- Chronic pain and discomfort
- Horner’s syndrome symptoms
- Blood pressure instability
- Impaired sweating and thermoregulation
Prevention
- Careful surgical techniques to avoid nerve damage
- Protective measures during trauma
- Early diagnosis and management of tumors or infections
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers specialized neurological and surgical care for sympathetic chain injuries:
- Diagnosis
- Clinical neurological examination
- Imaging studies such as MRI and CT scans
- Electrophysiological tests
- Medical Management
- Pain control with medications such as analgesics and neuropathic agents
- Symptomatic treatment for autonomic dysfunction
- Surgical Intervention
- Nerve repair or decompression surgery if indicated
- Tumor removal if compressive cause is identified
- Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy and occupational therapy
- Autonomic function monitoring and supportive care