Overview
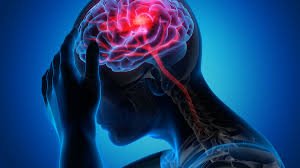
A stroke is a medical emergency caused by an interruption of blood flow to the brain, leading to brain cell damage or death. It can result in lasting neurological impairments or even death if not treated promptly. In Korea, stroke is one of the leading causes of death and long-term disability, but advanced hospital networks and national emergency response systems have significantly improved stroke survival and recovery rates.
What is Stroke?
A stroke, also called a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when the brain’s blood supply is disrupted, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This can happen due to a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or ruptured blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke). A related condition, transient ischemic attack (TIA) or “mini-stroke,” causes temporary stroke-like symptoms.
Stroke is classified into two main types:
- Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a blood clot or narrowing of arteries (accounts for about 80–85% of cases)
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Caused by bleeding in the brain due to a ruptured vessel
In Korea, ischemic stroke is more common, especially among the elderly population.
Symptoms
Stroke symptoms occur suddenly and may include:
- Numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg—especially on one side
- Confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination
- Severe headache with no known cause (more common in hemorrhagic stroke)
- Drooping on one side of the face
A helpful tool to recognize stroke symptoms is the F.A.S.T. test:
- Face drooping
- Arm weakness
- Speech difficulty
- Time to call emergency services (dial 119 in Korea)
Causes
The causes of stroke vary depending on the type:
- Ischemic stroke:
- Blood clots from the heart (cardioembolic stroke)
- Atherosclerosis (narrowing of arteries due to plaque)
- Hemorrhagic stroke:
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Brain aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations
- Head trauma
- Blood-thinning medications
Risk Factors
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of stroke, including:
- High blood pressure (major cause in Korea)
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease (atrial fibrillation, valve disease)
- Obesity and physical inactivity
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Family history of stroke
- Older age (risk increases after age 55)
Complications
If not treated promptly, stroke can lead to serious and lasting complications:
- Paralysis or muscle weakness (typically on one side of the body)
- Difficulty with speech or swallowing
- Memory loss or cognitive decline
- Depression or mood disorders
- Chronic pain or fatigue
- Risk of recurrent strokes
Prevention
Preventive strategies are critical and widely promoted in Korea through health screening programs:
- Monitor and control blood pressure regularly
- Manage diabetes and cholesterol
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a low-sodium, balanced diet
- Take medications as prescribed (especially for heart rhythm disorders)
- Undergo regular health checkups, particularly after age 40
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is known for its advanced stroke care, with designated Regional Cerebrovascular Centers and specialized stroke units across the country.
Diagnosis
- CT scan or MRI: To distinguish between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke
- Cerebral angiography: To evaluate blood vessel condition
- Carotid ultrasound: To check for narrowed arteries
- Blood tests and ECG: To identify underlying cardiac or metabolic issues
Medical Treatments
- Ischemic stroke:
- Thrombolytic therapy (tPA): Clot-dissolving medication given within 4.5 hours of symptom onset
- Antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel)
- Anticoagulants for strokes caused by atrial fibrillation
- Hemorrhagic stroke:
- Blood pressure control medications
- Drugs to reduce brain swelling or prevent seizures
All major Korean hospitals follow international stroke treatment guidelines and offer rapid intervention in emergency departments.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Endovascular thrombectomy: Removal of large clots via catheter (available at major stroke centers)
- Aneurysm clipping or coiling: For hemorrhagic strokes caused by ruptured aneurysms
- Craniotomy: To relieve pressure after severe brain swelling
- Korea offers minimally invasive neurosurgical options and robotic navigation systems in top hospitals
Rehabilitation and Support
- Physical therapy: To regain mobility and strength
- Speech and occupational therapy: For speech, memory, or swallowing issues
- Psychological counseling: To address emotional impact and depression
- Stroke recovery centers and community support programs are available in most cities