Overview
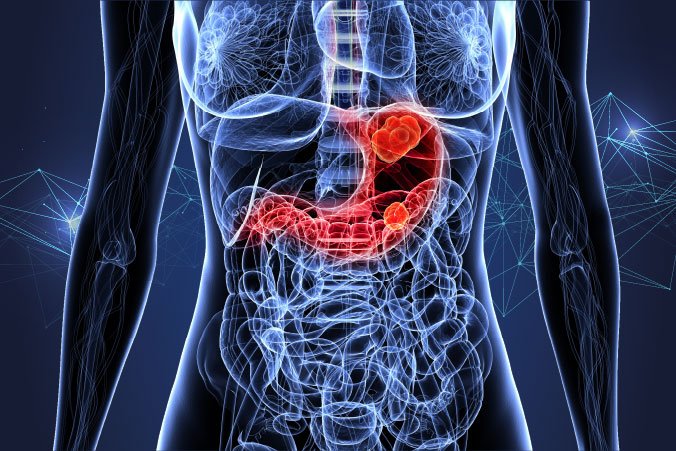
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a malignant tumor that develops from the lining of the stomach. Korea has one of the highest rates of stomach cancer globally, but it also has advanced screening programs and effective treatment options, contributing to improved survival rates.
What is Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer begins when abnormal cells in the stomach lining grow uncontrollably. The most common type is adenocarcinoma, which arises from the glandular cells of the stomach. The disease can progress silently in its early stages, making regular screening vital in high-risk populations like Korea.
Symptoms
Early-stage stomach cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Persistent indigestion or heartburn
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating after meals
- Nausea or vomiting
- Stomach pain or discomfort
- Difficulty swallowing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Vomiting blood or black, tarry stools (sign of internal bleeding)
Causes
- Helicobacter pylori infection (a major risk factor in Korea)
- Genetic mutations in stomach lining cells
- Chronic gastritis or intestinal metaplasia
- Previous stomach surgery
- Exposure to certain carcinogens (e.g., nitrosamines in preserved foods)
Risk Factors
- High intake of salted, smoked, or pickled foods (common in traditional Korean diets)
- Chronic H. pylori infection
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Family history of gastric cancer
- Age over 50
- Male gender
- History of gastric polyps or pernicious anemia
Complications
- Internal bleeding
- Gastric obstruction (blocking food from passing through the stomach)
- Metastasis to liver, lungs, or other organs
- Perforation of the stomach wall
- Nutritional deficiencies due to reduced stomach function
Prevention
- Early detection through regular screening programs (especially after age 40 in Korea)
- Treating H. pylori infections
- Reducing consumption of preserved, salty, or smoked foods
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake
- Eating more fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants
- Genetic counseling if there is a strong family history
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea is globally recognized for its advanced stomach cancer care, offering a full range of diagnostics and treatments:
- Screening and Diagnosis:
- Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy
- Biopsy and histopathological analysis
- CT scans and PET scans for staging
- Treatment Options:
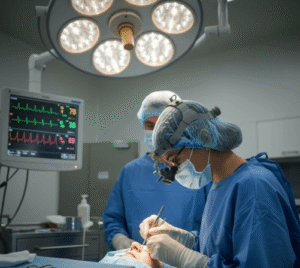
- Surgical resection (partial or total gastrectomy) with lymph node removal
- Chemotherapy (before or after surgery)
- Targeted therapy (e.g., trastuzumab for HER2-positive cancers)
- Radiation therapy
- Immunotherapy for advanced or metastatic cases