Overview
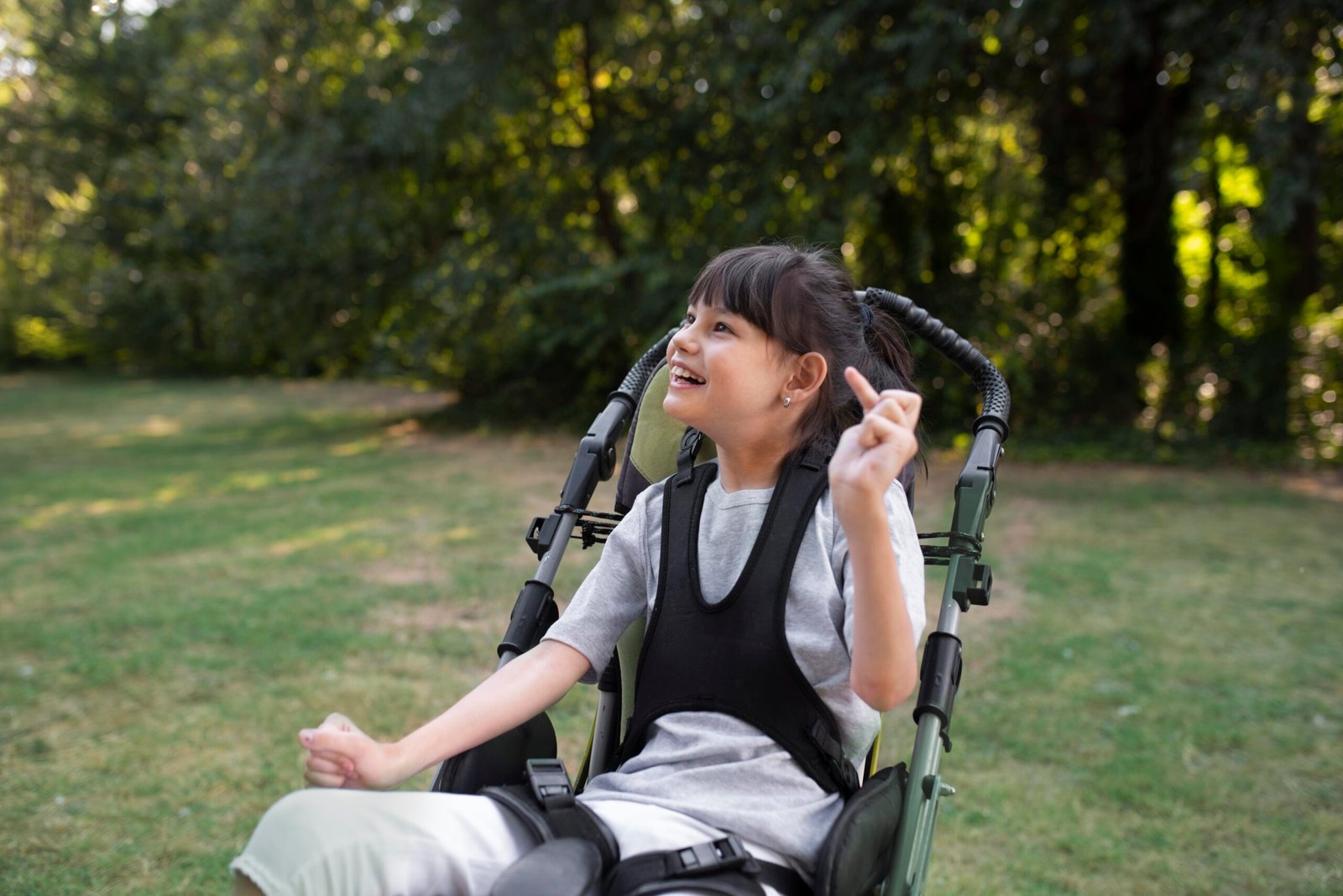
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a genetic neuromuscular disorder characterized by the progressive loss of motor neurons in the spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy. It is one of the leading genetic causes of infant mortality but can affect all ages depending on the type. South Korea provides advanced genetic testing, specialized multidisciplinary care, and access to novel treatments for SMA patients.
What is Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)?
SMA is caused by mutations in the SMN1 gene, which is critical for the survival of motor neurons. Loss of these neurons results in muscle wasting and weakness primarily affecting voluntary muscles used for movement, swallowing, and breathing. The severity varies from severe infantile forms to milder adult-onset types.
Symptoms
- Muscle weakness and decreased muscle tone (hypotonia)
- Difficulty in motor skills such as sitting, crawling, or walking
- Poor head control in infants
- Respiratory difficulties and frequent lung infections
- Swallowing and feeding challenges
- Muscle twitching (fasciculations)
Causes
- Genetic mutation in the SMN1 gene, inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern
- Reduced production of survival motor neuron (SMN) protein leading to motor neuron death
Risk Factors
- Family history of SMA
- Carrier parents (each must pass on the mutated gene)
- No known environmental factors; purely genetic
Complications
- Progressive muscle weakness leading to loss of mobility
- Respiratory failure due to weakened breathing muscles
- Feeding difficulties and risk of aspiration pneumonia
- Skeletal deformities such as scoliosis
- Reduced life expectancy in severe types without treatment
Prevention
- Genetic counseling for at-risk couples
- Prenatal and newborn screening programs (available in Korea)
- Early diagnosis and intervention to improve outcomes
Treatment Options in Korea
- Diagnosis
- Genetic testing for SMN1 gene mutation
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies
- Clinical evaluation by neurologists
- Medications and Therapies
- FDA-approved treatments available in Korea, such as:
- Nusinersen (Spinraza): An intrathecal injection improving SMN protein production
- Onasemnogene abeparvovec (Zolgensma): Gene therapy for infants
- Risdiplam (Evrysdi): Oral medication increasing SMN protein
- Supportive treatments for respiratory care, nutrition, and physical therapy
- Multidisciplinary Care
- Specialized SMA clinics in major Korean hospitals provide coordinated care from neurologists, pulmonologists, nutritionists, and rehabilitation specialists
- Respiratory support including non-invasive ventilation
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy programs
- Rehabilitation and Support
- Customized exercises to maintain muscle function
- Assistive devices like wheelchairs or braces
- Psychological and social support for patients and families