Overview
Rothmund-Thomson Syndrome (RTS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by distinctive skin changes, skeletal abnormalities, growth delay, and an increased risk of developing certain cancers. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary care are essential for managing symptoms and monitoring for complications. In Korea, specialized genetic and pediatric centers provide comprehensive evaluation and personalized management for RTS patients.
What is Rothmund-Thomson Syndrome?
RTS is caused by mutations in the RECQL4 gene, leading to defects in DNA repair mechanisms. This results in the characteristic skin rash, skeletal malformations, and predisposition to bone cancers like osteosarcoma. The syndrome typically presents in infancy or early childhood.
Symptoms
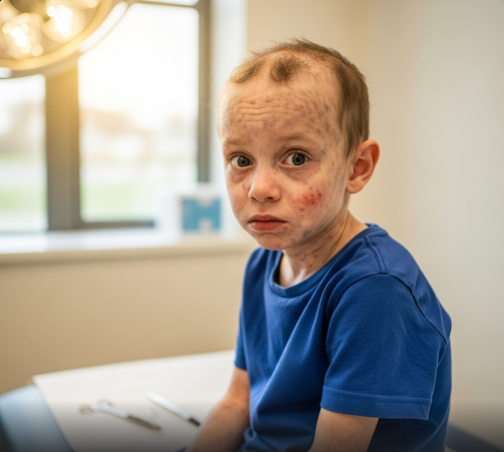
- Poikiloderma: a rash with redness, pigmentation changes, and thinning of the skin, usually starting on the face and spreading
- Sparse or absent hair, eyelashes, and eyebrows
- Small stature and growth delays
- Skeletal abnormalities such as absent or malformed bones, especially thumbs and forearms
- Cataracts and other eye abnormalities
- Increased risk of osteosarcoma and other malignancies
- Dental anomalies and delayed tooth eruption
Causes
- Autosomal recessive mutations in the RECQL4 gene affecting DNA helicase function
- Resulting in impaired DNA repair and cellular instability
Risk Factors
- Family history of RTS or related genetic conditions
- Consanguineous parentage increases risk
Complications
- Increased susceptibility to bone cancers, particularly osteosarcoma
- Skeletal deformities impacting function and mobility
- Vision problems due to cataracts
- Delayed growth and developmental issues
Prevention
- Genetic counseling for affected families
- Early screening for malignancies and skeletal problems
- Avoidance of environmental factors that cause DNA damage, such as excessive UV exposure
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean medical centers offer multidisciplinary care for RTS:
- Dermatology Care: Management of skin symptoms with sun protection and topical treatments.
- Orthopedic Management: Surgical and supportive treatments for skeletal abnormalities.
- Oncology Surveillance: Regular monitoring for early detection of cancers.
- Ophthalmology Care: Treatment and monitoring of eye abnormalities.
- Genetic Counseling: Family education on inheritance, risks, and reproductive options.
- Supportive Therapies: Nutritional support, physical therapy, and developmental interventions.