Overview
A Rotator Cuff Tear is a common injury involving a tear in one or more of the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles in the shoulder. This injury leads to pain, weakness, and limited range of motion in the shoulder. In Korea, orthopedic specialists provide advanced diagnostic tools and both surgical and non-surgical treatment options to restore shoulder function and reduce pain.
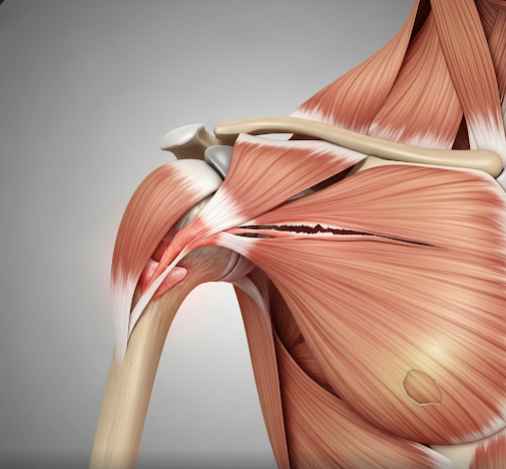
What is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and enable arm movements. A tear occurs when one or more of these tendons are partially or completely torn due to injury, degeneration, or overuse.
Symptoms
- Shoulder pain, especially when lifting the arm or at night
- Weakness or difficulty lifting or rotating the arm
- Limited range of motion
- A cracking or popping sensation in the shoulder
- Muscle atrophy in chronic cases
Causes
- Acute injury such as falling on an outstretched arm or lifting heavy objects
- Degenerative changes due to aging and repetitive overhead activities
- Poor posture or biomechanics contributing to tendon wear
- Repetitive stress in sports or occupations involving overhead arm movements
Risk Factors
- Age over 40 years
- Repetitive overhead activities (sports like baseball, swimming, or occupations like painting)
- Previous shoulder injuries
- Poor physical conditioning or muscle imbalances
Complications
- Chronic shoulder pain and disability
- Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) due to disuse
- Progressive tendon degeneration and muscle weakness
- Difficulty performing daily activities or sports
Prevention
- Strengthening shoulder muscles with targeted exercises
- Avoiding repetitive overhead motions without adequate rest
- Proper technique and ergonomics in sports and work
- Early treatment of shoulder pain or injuries
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean orthopedic centers offer comprehensive care for rotator cuff tears:
- Conservative Management: Rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and steroid injections for mild to moderate tears.
- Imaging Diagnostics: MRI or ultrasound to assess tear size and tendon condition.
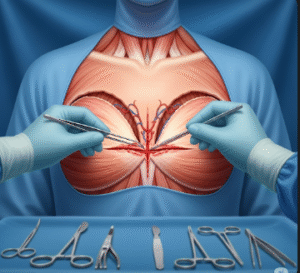
- Surgical Repair: Arthroscopic or open surgery to reattach torn tendons in larger or refractory tears.
- Postoperative Rehabilitation: Customized physical therapy programs to restore strength and flexibility.
- Advanced Therapies: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections or stem cell therapy as adjunct treatments in select cases.