Overview
Roseola infantum, also known as sixth disease, is a common viral infection that primarily affects infants and young children between 6 months and 2 years old. It is caused by human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and sometimes HHV-7. The illness is generally mild and self-limiting, characterized by a sudden high fever followed by a distinctive rash as the fever subsides.
What is Roseola Infantum?
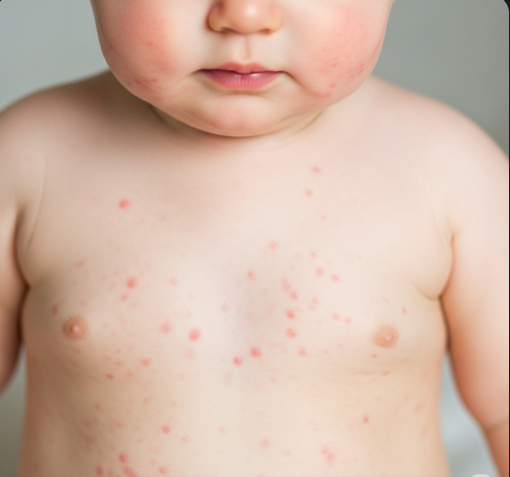
Roseola infantum is an acute viral infection presenting with a rapid onset of high fever lasting three to five days, which then resolves abruptly, followed by the appearance of a pinkish rash mainly on the trunk and neck. The condition is highly contagious but usually resolves without serious complications. It is most common in infants and toddlers and rarely affects older children or adults.
Symptoms
Typical symptoms include:
- Sudden high fever (often above 39.5°C or 103°F) lasting 3-5 days
- Irritability and mild respiratory symptoms like runny nose or cough
- Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the neck
- After fever resolves, a pink, flat or raised rash appears, starting on the trunk and spreading to limbs and face
- Decreased appetite and mild diarrhea in some cases
Causes
Roseola infantum is caused by infection with human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), and less commonly HHV-7. These viruses spread through respiratory secretions or saliva from infected individuals. Most children contract the virus before the age of two, often from close contact with siblings or other children.
Risk Factors
Factors increasing risk include:
- Age between 6 months and 2 years
- Close contact with other infected children or caregivers
- Attendance at daycare centers or crowded environments
- Weakened immune system (rarely)
Complications
Roseola infantum is usually mild, but rare complications may include:
- Febrile seizures due to high fever
- Encephalitis or meningitis (very rare)
- Secondary bacterial infections due to weakened immune response
Prevention
There is no vaccine for roseola infantum, but prevention tips include:
- Practicing good hand hygiene among caregivers and children
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals during the contagious period
- Keeping the child home during fever phase to prevent spread
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment of roseola infantum in South Korea focuses on supportive care and monitoring.
1. Fever Management – Use of acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce fever and discomfort.
2. Hydration – Encouraging fluids to prevent dehydration during fever.
3. Monitoring for Seizures – Parents are advised on how to recognize and respond to febrile seizures.
4. Hospital Care – Rarely needed unless complications arise; Korean pediatric hospitals provide emergency care and monitoring for severe cases.
5. Traditional Korean Medicine – Some families opt for gentle herbal remedies and acupuncture to soothe symptoms under professional guidance.
6. Leading Korean Pediatric Centers for Roseola Care
- Seoul National University Children’s Hospital
- Samsung Medical Center – Pediatric Department
- Asan Medical Center – Pediatric Infectious Disease Unit
- Severance Hospital – Pediatric Clinic