Overview
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) is a serious tick-borne infectious disease caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii. It leads to fever, rash, and potentially life-threatening complications if not treated promptly. Though more common in North America, RMSF cases are rare but possible in travelers or imported ticks. In Korea, infectious disease specialists are well-prepared to diagnose and manage RMSF and other tick-borne illnesses.
What is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
RMSF is caused by Rickettsia rickettsii, transmitted through the bite of infected ticks. The bacteria infect the lining of small blood vessels, causing widespread inflammation, rash, and damage to multiple organs. Early treatment is critical to prevent severe outcomes.
Symptoms
- Sudden high fever and chills
- Severe headache
- Muscle aches and fatigue
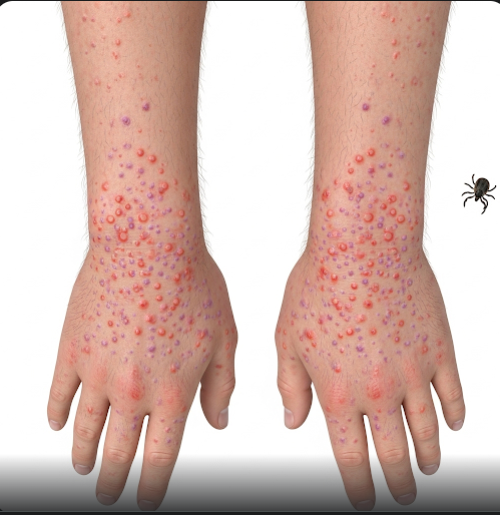
- Rash beginning 2-5 days after fever, typically starting on wrists and ankles and spreading to the trunk
- Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain
- Confusion or neurological symptoms in severe cases
Causes
- Bite from infected ticks such as the American dog tick, Rocky Mountain wood tick, or brown dog tick
- Bacteria Rickettsia rickettsii entering the bloodstream
Risk Factors
- Outdoor activities in tick-infested areas
- Exposure to wooded or grassy regions
- Not using tick repellents or protective clothing
- Delayed removal of ticks
Complications
- Organ failure (kidneys, lungs, heart)
- Meningitis or encephalitis
- Amputation due to poor blood flow
- Death if untreated or treatment is delayed
Prevention
- Use of insect repellents containing DEET
- Wearing long sleeves and pants in tick-infested areas
- Regular tick checks after outdoor exposure
- Prompt removal of attached ticks with proper technique
- Avoiding high-risk areas during peak tick seasons
Treatment Options in Korea
Though rare, Korean infectious disease units follow international guidelines for RMSF:
- Antibiotic Therapy: Early treatment with doxycycline is the gold standard, even in children and pregnant women when benefits outweigh risks.
- Supportive Care: Management of symptoms and organ support in severe cases.
- Hospitalization: For monitoring and treating complications.
- Tick Bite Management: Education on prevention and early signs of tick-borne diseases.