Overview
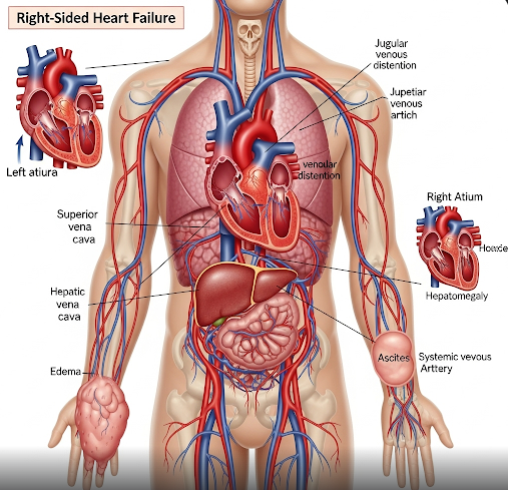
Right-Sided Heart Failure is a condition where the right side of the heart is unable to pump blood effectively, causing blood to back up into the veins and leading to fluid buildup in the body. It often results from left-sided heart failure or lung diseases. In Korea, advanced cardiology services provide comprehensive diagnosis and tailored treatment to manage symptoms and improve patient outcomes.
What is Right-Sided Heart Failure?
Right-sided heart failure occurs when the right ventricle cannot pump blood efficiently to the lungs, causing blood to accumulate in the systemic circulation. This leads to swelling in the legs, abdomen, and other parts of the body. It can be isolated or, more commonly, occur alongside left-sided heart failure.
Symptoms
- Swelling (edema) in legs, ankles, and abdomen
- Shortness of breath, especially during exertion
- Fatigue and weakness
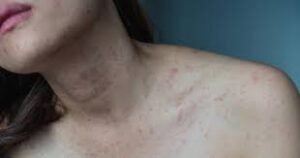
- Jugular vein distension (visible neck veins)
- Weight gain due to fluid retention
- Increased urination at night
Causes
- Left-sided heart failure leading to increased pressure in lungs
- Chronic lung diseases such as COPD or pulmonary hypertension
- Right ventricular myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Congenital heart defects affecting the right heart
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clot in lungs)
Risk Factors
- History of left-sided heart failure
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or other lung diseases
- Coronary artery disease
- High blood pressure
- Heart valve diseases
Complications
- Severe fluid retention causing difficulty breathing and mobility issues
- Liver congestion and dysfunction
- Kidney impairment due to poor circulation
- Arrhythmias and sudden cardiac events
Prevention
- Managing underlying causes like left-sided heart failure and lung diseases
- Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol
- Smoking cessation and healthy lifestyle
- Regular medical check-ups and cardiac evaluations
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean cardiology centers offer comprehensive care for right-sided heart failure:
- Medications: Diuretics to reduce fluid overload, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and vasodilators to improve heart function.
- Lifestyle Management: Dietary sodium restriction, exercise programs, and fluid intake control.
- Treatment of Underlying Causes: Management of lung diseases, heart valve repair, or coronary interventions.
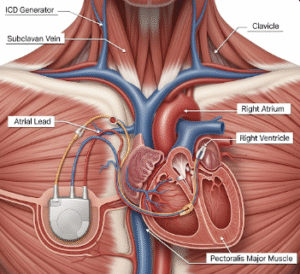
- Advanced Therapies: Use of devices like pacemakers or ventricular assist devices in severe cases.
- Monitoring: Regular echocardiography and clinical assessments to guide treatment adjustments.