Overview
A rib fracture is a common injury involving a break or crack in one or more of the rib bones, usually caused by trauma to the chest. While most rib fractures heal on their own, they can cause significant pain and sometimes lead to complications such as lung injury. In Korea, advanced trauma care and pain management help patients recover effectively and minimize complications.
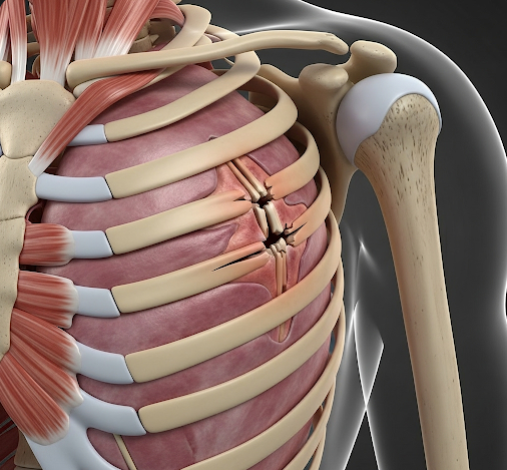
What is a Rib Fracture?
A rib fracture occurs when a rib bone is broken or cracked, typically due to blunt chest trauma, such as a fall, motor vehicle accident, or direct blow. Rib fractures can vary from simple cracks to multiple broken ribs, sometimes causing instability in the chest wall.
Symptoms
- Sharp, severe pain at the site of injury, worsened by breathing or coughing
- Tenderness and swelling over the fractured rib
- Difficulty breathing deeply due to pain
- Bruising on the chest wall
- In severe cases, deformity or chest wall instability
Causes
- Blunt trauma to the chest (falls, car accidents, sports injuries)
- Severe coughing or repetitive stress (rare)
- Pathological fractures due to underlying bone diseases (osteoporosis, cancer)
Risk Factors
- Elderly individuals with more fragile bones
- Osteoporosis or other metabolic bone diseases
- High-impact accidents or injuries
- Sports involving contact or high risk of falls
Complications
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
- Hemothorax (bleeding in the chest cavity)
- Pulmonary contusion (lung bruising)
- Pneumonia due to shallow breathing and poor cough
- Flail chest in multiple rib fractures causing chest instability
Prevention
- Use of protective gear in high-risk activities and sports
- Fall prevention strategies for the elderly
- Maintaining bone health through diet, exercise, and osteoporosis treatment
- Safe driving practices and accident prevention
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean trauma and orthopedic centers provide comprehensive care for rib fractures:
- Pain Management:
- Oral and injectable pain relievers
- Nerve blocks or epidural analgesia for severe pain
- Respiratory Support:
- Encouragement of deep breathing exercises and coughing to prevent lung complications
- Oxygen therapy if needed
- Imaging: Chest X-rays or CT scans to assess fracture extent and complications
- Surgical Intervention:
- Rarely needed but performed for flail chest or severely displaced fractures
- Rib fixation using plates and screws to stabilize the chest wall
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy to restore respiratory function and mobility