Overview
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can develop as a complication of untreated or inadequately treated streptococcal throat infection (strep throat). It primarily affects children and young adults and can cause long-term damage to the heart, joints, and other tissues. In Korea, prompt diagnosis and effective antibiotic treatment help prevent rheumatic fever and its complications, with comprehensive care available for affected patients.
What is Rheumatic Fever?
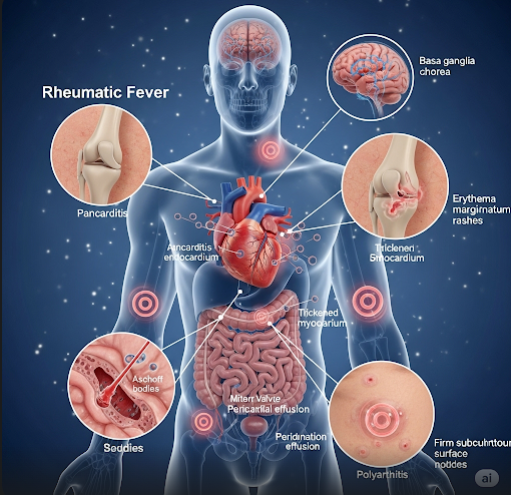
Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune reaction triggered by a group A Streptococcus bacterial infection. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, particularly the heart valves, joints, skin, and brain, leading to inflammation and damage. Without treatment, it can lead to rheumatic heart disease.
Symptoms
- Fever
- Painful and swollen joints (arthritis), often migrating from one joint to another
- Heart inflammation (carditis) causing chest pain, shortness of breath, or heart murmurs
- Skin rash (erythema marginatum)
- Small, painless nodules under the skin (subcutaneous nodules)
- Involuntary muscle movements (Sydenham chorea)
Causes
- Untreated or poorly treated infection with group A Streptococcus bacteria (strep throat or scarlet fever)
- Immune system cross-reaction attacking body tissues
Risk Factors
- Children aged 5 to 15 years (most commonly affected)
- Living in crowded or low-income conditions with limited access to healthcare
- Recurrent streptococcal infections
Complications
- Rheumatic heart disease (permanent damage to heart valves)
- Heart failure
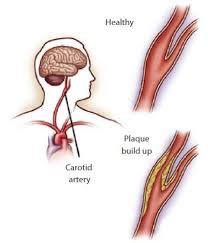
- Stroke (due to heart complications)
- Recurring episodes of rheumatic fever leading to progressive heart damage
Prevention
- Prompt diagnosis and full course of antibiotics for strep throat
- Regular medical check-ups in high-risk populations
- Secondary prophylaxis with long-term antibiotics to prevent recurrence in patients with a history of rheumatic fever
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean healthcare facilities provide comprehensive management of rheumatic fever:
- Antibiotics: Penicillin or alternative antibiotics to eradicate streptococcal infection.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Aspirin or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
- Cardiac Care: Monitoring and treatment for carditis, including medications or surgery if valve damage occurs.
- Long-term Prophylaxis: Regular antibiotic injections or oral antibiotics to prevent recurrent rheumatic fever.
- Rehabilitation and Support: Physical therapy for joint symptoms and patient education for disease management.