Overview
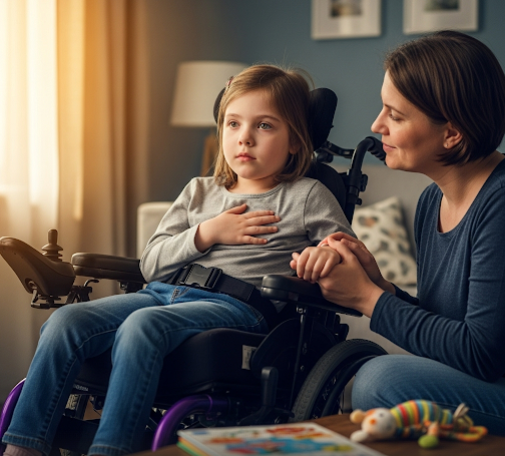
Rett Syndrome is a rare genetic neurological disorder that primarily affects girls and leads to severe cognitive, motor, and communication impairments. It usually becomes apparent after 6 to 18 months of normal early development. In Korea, advanced genetic testing, multidisciplinary care, and supportive therapies are available to improve quality of life and manage symptoms in individuals with Rett Syndrome.
What is Rett Syndrome?
Rett Syndrome is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene on the X chromosome. It is characterized by a period of normal development followed by a loss of acquired skills such as speech and purposeful hand use. The disorder leads to impaired brain development and function, resulting in severe disability.
Symptoms
- Loss of purposeful hand skills and repetitive hand movements (wringing, clapping)
- Loss of spoken language
- Intellectual disability and cognitive decline
- Motor difficulties including ataxia and spasticity
- Breathing irregularities (hyperventilation, apnea)
- Seizures
- Scoliosis and growth retardation
- Social withdrawal and autistic-like behaviors
Causes
- Mutation in the MECP2 gene on the X chromosome
- Mostly occurs spontaneously (de novo mutations)
- Rarely inherited
Risk Factors
- Female gender (almost exclusively affects girls)
- Family history is rare as most cases are spontaneous mutations
Complications
- Severe physical and intellectual disability
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders
- Scoliosis and orthopedic issues
- Breathing difficulties leading to respiratory infections
- Nutritional problems due to swallowing difficulties
- Reduced life expectancy in severe cases
Prevention
- No known prevention due to genetic nature
- Genetic counseling for families with history of MECP2 mutations
Treatment Options in Korea
Although there is no cure for Rett Syndrome, Korea offers multidisciplinary care to support affected individuals:
- Genetic Testing and Counseling: Early diagnosis through genetic screening to confirm MECP2 mutation.
- Symptom Management: Medications to control seizures, muscle tone abnormalities, and breathing irregularities.
- Rehabilitation Therapies: Physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and behavioral therapy to maximize function and communication.
- Nutritional Support: Feeding interventions to manage swallowing difficulties and maintain adequate nutrition.
- Specialized Care: Coordination among neurologists, pediatricians, therapists, and social workers for comprehensive care.
- Research and Clinical Trials: Access to cutting-edge research studies exploring potential therapies.