Overview
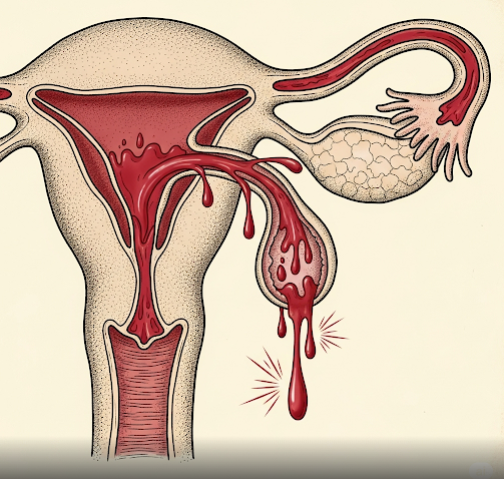
Retrograde menstruation is a condition in which menstrual blood flows backward into the pelvic cavity through the fallopian tubes instead of leaving the body through the vagina. This backward flow can carry endometrial cells into the pelvis, which may attach to pelvic organs and cause endometriosis. In Korea, early detection and treatment of retrograde menstruation are supported by advanced gynecological diagnostic techniques and minimally invasive surgical options.
What is Retrograde Menstruation?
Retrograde menstruation occurs when some or all of the menstrual flow moves in the reverse direction, toward the fallopian tubes and pelvic cavity. While it can happen to many women without causing problems, in some cases, it leads to the development of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, contributing to pelvic pain, infertility, and other reproductive health issues.
Symptoms
- Painful menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea)
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding
- Infertility issues
- Symptoms related to endometriosis, if present
Causes
- Anatomical abnormalities of the uterus, cervix, or fallopian tubes
- Hormonal imbalances affecting menstrual flow
- Narrow cervical canal or blockage in menstrual outflow
- Pelvic surgery or scarring
- Genetic predisposition
Risk Factors
- Family history of endometriosis
- Early onset of menstruation (menarche)
- Long menstrual cycles or heavy bleeding
- Short menstrual cycles (less than 27 days)
- Structural abnormalities of the reproductive tract
Complications
- Development of endometriosis
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Infertility
- Formation of pelvic adhesions
- Ovarian cysts (endometriomas)
Prevention
- Regular gynecological check-ups for early detection
- Maintaining hormonal balance through lifestyle and medical management
- Prompt treatment of menstrual irregularities
- Considering hormonal therapies to regulate menstrual cycles in high-risk patients
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean gynecological care focuses on accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment for retrograde menstruation:
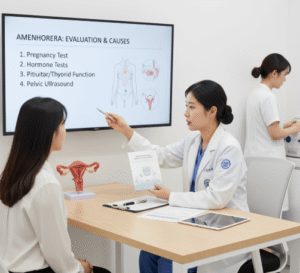
- Diagnostic Methods: Laparoscopy, pelvic ultrasound, MRI, and hysteroscopy to detect endometriosis and structural abnormalities.
- Medications: Hormonal therapies like birth control pills, progestins, and GnRH agonists to reduce menstrual flow and prevent backward bleeding.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery to remove endometrial implants and correct anatomical abnormalities.
- Pain Management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and physiotherapy for symptom relief.
- Fertility Support: Assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF for patients experiencing infertility due to retrograde menstruation-related endometriosis.