Overview
Retrograde ejaculation is a condition in which semen flows backward into the bladder instead of exiting through the urethra during ejaculation. Although it does not cause pain or affect the ability to have an orgasm, it can lead to infertility issues. In Korea, advanced urological evaluation and treatment options are available to diagnose and manage retrograde ejaculation effectively.
What is Retrograde Ejaculation?
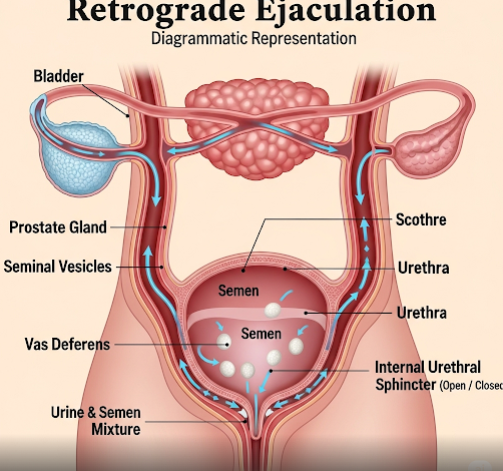
Retrograde ejaculation occurs when the bladder neck fails to close properly during ejaculation, allowing semen to travel backward into the bladder instead of being expelled outside the body. This can result from nerve damage, surgery, medications, or other medical conditions affecting the urinary or reproductive systems.
Symptoms
- Little or no semen released during ejaculation (dry orgasm)
- Cloudy urine after ejaculation (due to presence of semen in urine)
- Normal sexual function and orgasmic sensation
- Possible infertility due to lack of semen expulsion
Causes
- Nerve damage from diabetes or spinal cord injury
- Side effects of medications such as alpha-blockers or antidepressants
- Prostate or bladder surgery, including transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
- Neurological disorders affecting bladder neck control
- Chronic inflammation or infection affecting urinary tract
Risk Factors
- Diabetes mellitus
- History of pelvic or prostate surgery
- Use of certain medications
- Multiple sclerosis or other neurological diseases
- Aging
Complications
- Infertility due to reduced or absent semen ejaculation
- Psychological distress related to sexual function or fertility concerns
Prevention
- Careful management of diabetes and neurological conditions
- Discussing medication side effects with healthcare providers
- Proper surgical techniques to minimize nerve damage during prostate or bladder surgeries
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean urology centers offer advanced diagnosis and treatment for retrograde ejaculation:
- Diagnostic Tests: Urinalysis after ejaculation to detect sperm presence, semen analysis, and neurological evaluation.
- Medication Adjustment: Changing or stopping medications that contribute to retrograde ejaculation when possible.
- Medications: Drugs like pseudoephedrine or imipramine to strengthen bladder neck closure.
- Assisted Reproductive Techniques: Sperm retrieval from urine followed by procedures such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) for fertility treatment.
- Counseling: Psychological support and counseling to address concerns related to sexual health and fertility.