Overview
Retinoschisis is a retinal condition characterized by the splitting of the retinal layers, which can lead to visual disturbances and, in some cases, vision loss. While often benign and stable, certain types of retinoschisis may progress or cause complications. In Korea, advanced ophthalmic diagnostic tools and expert care are available to monitor and manage this condition effectively.
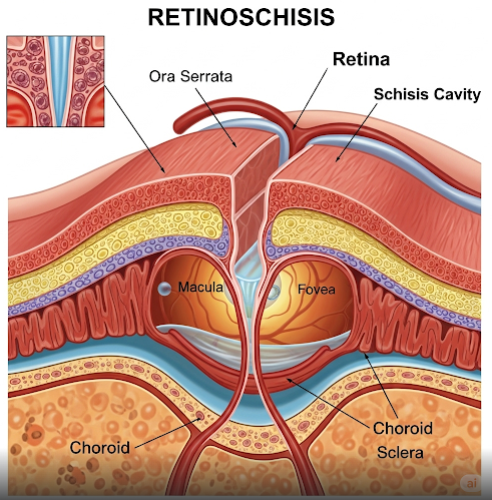
What is Retinoschisis?
Retinoschisis refers to the splitting or separation of the retina’s neurosensory layers, typically in the peripheral retina. It can be congenital (juvenile retinoschisis) or acquired, and unlike retinal detachment, it usually does not involve a full-thickness break. The condition can cause visual field defects and, rarely, more serious complications.
Symptoms
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision
- Blurred or distorted vision in affected areas
- Often asymptomatic in early stages
- Occasionally, flashes of light or floaters if complications arise
Causes
- Genetic mutations, especially in juvenile retinoschisis (often X-linked)
- Age-related degenerative changes in the retina
- Trauma or other eye diseases may contribute in some cases
Risk Factors
- Family history of retinoschisis
- Male gender (juvenile retinoschisis mostly affects males)
- Age (degenerative retinoschisis is more common in older adults)
- High myopia
Complications
- Retinal detachment if full-thickness breaks develop
- Vision loss in affected retinal areas
- Macular involvement leading to central vision impairment
- Secondary vitreous hemorrhage in rare cases
Prevention
- Regular eye exams for individuals with family history or risk factors
- Prompt evaluation of any new visual symptoms
- Protective eyewear to prevent trauma-related complications
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean eye care centers provide comprehensive monitoring and treatment strategies for retinoschisis:
- Diagnostic Imaging: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus photography to accurately diagnose and monitor retinal splitting.
- Observation: Most cases require careful monitoring without immediate treatment if asymptomatic and stable.
- Laser Therapy: Used in select cases to prevent progression or treat associated retinal tears.
- Surgical Intervention: Rarely needed but performed in complicated cases with retinal detachment or severe vision loss.
- Low Vision Support: For patients with significant vision impairment, Korean clinics offer vision rehabilitation and aids.