Overview
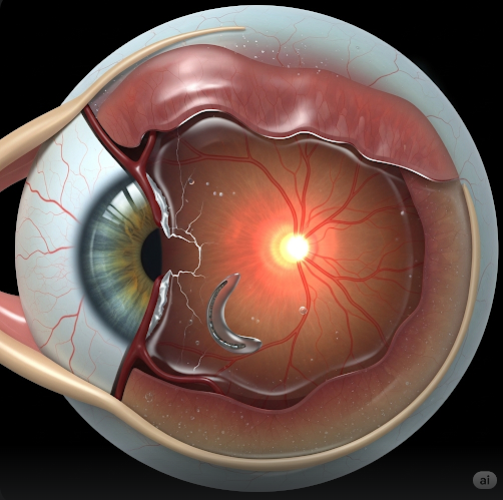
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition where the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye, separates from its underlying supportive tissue. This separation can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly. In Korea, retinal detachment is treated with advanced diagnostic imaging and highly specialized surgical techniques, making the country a sought-after destination for eye care and vision restoration.
What is Retinal Detachment?
Retinal detachment occurs when fluid passes through a retinal tear, lifting the retina away from the choroid (its nourishing tissue). Without quick treatment, the affected part of the retina cannot function, leading to vision impairment or blindness.
Symptoms
- Sudden appearance of floaters (small spots in vision)
- Flashes of light in one or both eyes
- A shadow or curtain-like effect over part of the visual field
- Blurred vision
Causes
- Retinal tears or holes
- Severe myopia (nearsightedness)
- Eye injury or trauma
- Aging-related vitreous changes
- Complications from eye surgery
- Inflammatory eye diseases
Risk Factors
- Age over 50
- Family history of retinal detachment
- Prior eye surgery (e.g., cataract surgery)
- Eye trauma
- High myopia
- Diabetes-related retinopathy
Complications
- Permanent vision loss if untreated
- Recurrence of detachment
- Macular damage affecting central vision
- Development of scar tissue on the retina
Prevention
- Regular eye exams, especially for high-risk individuals
- Prompt treatment of retinal tears or holes
- Wearing protective eyewear during high-risk activities
- Managing underlying conditions like diabetes
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
- Fundus photography
- Ultrasound B-scan for opaque media cases
Medical Treatments
- Not typically effective for full detachment, but laser therapy or cryotherapy may be used to treat small tears before detachment occurs
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Pneumatic Retinopexy – Injecting a gas bubble into the eye to push the retina back in place
- Scleral Buckling – Placing a silicone band around the eye to relieve retinal traction
- Vitrectomy – Removing vitreous gel and replacing it with saline, gas, or silicone oil to reattach the retina
- Combination procedures for complex cases
Rehabilitation and Support
- Post-surgery positioning (face-down) to maintain retinal attachment
- Vision therapy for partial vision recovery
- Regular monitoring for recurrence
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Ophthalmology Center
- Asan Medical Center – Retina and Vitreous Clinic
- Samsung Medical Center – Eye Hospital Division
- B&VIIT Eye Center – Specialized in retinal surgeries