Overview
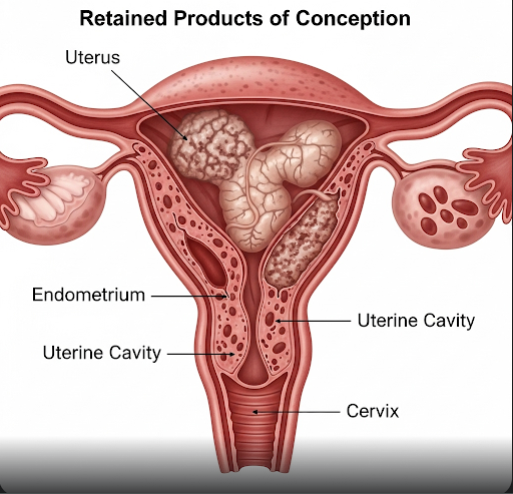
Retained Products of Conception (RPOC) is a condition where placental or fetal tissue remains inside the uterus after a miscarriage, abortion, or childbirth. This can lead to complications such as infection, heavy bleeding, and prolonged recovery if not properly managed. In Korea, advanced diagnostic tools and effective treatment methods are widely available to ensure safe and complete removal of retained tissue, minimizing risks and supporting women’s reproductive health.
What is Retained Products of Conception?
Retained Products of Conception refer to the remnants of placental or fetal tissue that remain in the uterus following pregnancy loss or delivery. These tissues can cause persistent bleeding, infection, and uterine inflammation, making timely diagnosis and treatment crucial to prevent further complications.
Symptoms
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting that continues or returns after miscarriage or delivery
- Lower abdominal pain or cramping
- Fever or chills (indicating infection)
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Delayed uterine involution (uterus not shrinking back to normal size)
Causes
- Incomplete miscarriage or abortion
- Retention of placental fragments after childbirth or cesarean section
- Previous uterine surgery or trauma
- Infection during or after delivery
Risk Factors
- History of miscarriage or incomplete abortion
- Uterine abnormalities (such as fibroids or scarring)
- Infection during pregnancy or postpartum period
- Induced abortion or surgical procedures involving the uterus
- Advanced maternal age
Complications
- Heavy and prolonged vaginal bleeding leading to anemia
- Uterine infection (endometritis) which can spread if untreated
- Formation of intrauterine adhesions (Asherman’s syndrome) causing fertility issues
- Sepsis in severe untreated infections
- Delayed recovery of normal menstrual cycles
Prevention
- Early and accurate diagnosis of miscarriage or incomplete abortion
- Careful monitoring after delivery or pregnancy termination
- Proper hygiene and infection control measures during and after delivery or procedures
- Prompt medical consultation if abnormal bleeding or pain occurs
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers state-of-the-art treatment options for RPOC, focusing on safe and effective removal of retained tissue to prevent complications and preserve fertility.
- Ultrasound Diagnosis: Advanced transvaginal ultrasound is used for precise detection and assessment of retained tissue.
- Medical Management: In selected cases, medications like misoprostol may be used to help expel retained tissue naturally.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C): A common surgical procedure to scrape out retained tissue under anesthesia.
- Hysteroscopic Removal: A minimally invasive surgery using a camera and instruments to directly visualize and remove tissue, reducing risks and improving outcomes.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Administered to prevent or treat infection when necessary.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring through ultrasound and clinical exams to ensure complete recovery.