Overview
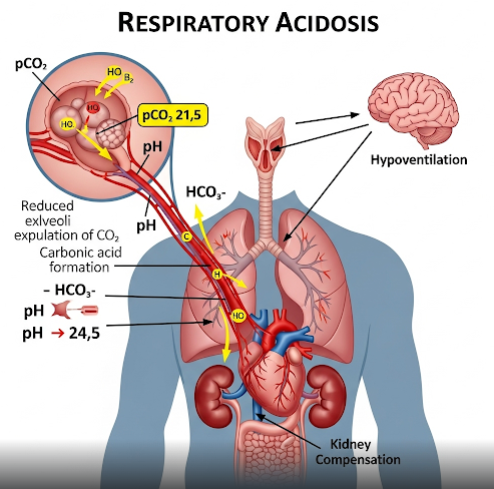
Respiratory acidosis is a condition characterized by an excess of carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the blood due to inadequate ventilation, leading to a decrease in blood pH (acidosis). It can result from various respiratory disorders that impair lung function. Korea provides advanced diagnostic facilities and comprehensive treatment options for managing respiratory acidosis effectively.
What is Respiratory Acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis occurs when the lungs cannot remove enough CO₂ produced by the body, causing it to accumulate in the bloodstream. This leads to a disturbance in the body’s acid-base balance, resulting in decreased blood pH.
Symptoms
- Shortness of breath or rapid breathing
- Confusion or drowsiness
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Cyanosis (bluish skin coloration) in severe cases
- Tachycardia and arrhythmias
Causes
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Severe asthma attacks
- Respiratory muscle weakness (e.g., neuromuscular diseases)
- Drug overdose causing respiratory depression
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Chest wall deformities or trauma
Risk Factors
- Smoking and exposure to lung irritants
- Chronic lung diseases
- Neurological or muscular disorders affecting breathing
- Use of sedatives or narcotics
Complications
- Respiratory failure
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Coma in severe untreated cases
- Chronic respiratory acidosis can lead to compensatory kidney changes and electrolyte imbalances
Prevention
- Management of chronic lung diseases
- Avoidance of smoking and pollutants
- Regular medical follow-up for respiratory conditions
- Timely treatment of infections and exacerbations
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis to measure CO₂ and blood pH
- Pulmonary function tests to assess lung capacity
- Chest X-rays and CT scans to identify underlying lung pathology
- Monitoring oxygen and carbon dioxide levels
Medical Treatments
- Oxygen therapy to maintain adequate oxygenation
- Bronchodilators and corticosteroids for obstructive lung diseases
- Mechanical ventilation for severe respiratory failure
- Treatment of underlying causes such as infections or neuromuscular conditions
Interventional & Surgical Treatments
- Non-invasive ventilation (e.g., CPAP or BiPAP) for chronic respiratory failure
- Tracheostomy in selected cases with prolonged ventilation needs
Advanced Therapies
- Pulmonary rehabilitation programs to improve lung function
- Use of advanced ventilators with tailored settings for patient comfort and efficiency
- Multidisciplinary care involving pulmonologists, respiratory therapists, and critical care specialists
Rehabilitation and Support
- Respiratory therapy and breathing exercises
- Nutritional support to enhance respiratory muscle strength
- Psychological counseling for chronic respiratory illness
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea for Respiratory Acidosis
- Seoul National University Hospital – Comprehensive pulmonology and critical care services
- Asan Medical Center – Advanced respiratory therapy and ventilation support
- Samsung Medical Center – Expertise in lung diseases and respiratory failure
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Integrated pulmonary and intensive care
- Korea University Anam Hospital – Specialized in chronic respiratory conditions