Overview
Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a group of rare disorders characterized by the kidneys’ inability to properly acidify the urine, leading to a buildup of acid in the blood (metabolic acidosis). This condition affects the renal tubules’ function and can cause growth retardation, kidney stones, bone disease, and other metabolic complications. Korea provides expert diagnosis and tailored treatment options for managing RTA effectively.
What is Renal Tubular Acidosis?
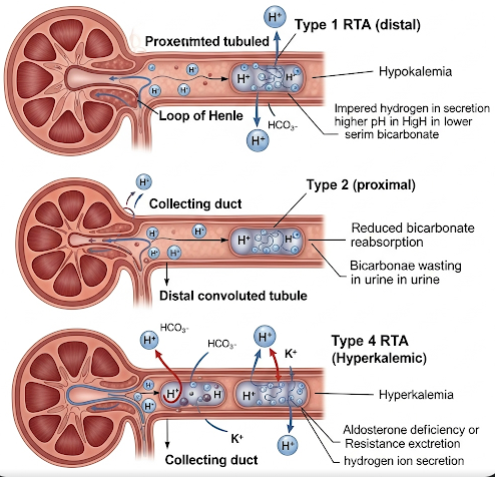
Renal tubular acidosis is a disorder where the renal tubules fail to adequately excrete hydrogen ions or reabsorb bicarbonate, resulting in chronic metabolic acidosis. There are several types of RTA, including distal (Type 1), proximal (Type 2), and mixed (Type 4), each with distinct pathophysiology and clinical features.
Symptoms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Growth delay in children
- Bone pain or deformities (rickets or osteomalacia)
- Kidney stones or nephrocalcinosis
- Muscle cramps and dehydration
- Increased urination and thirst
Causes
- Genetic mutations affecting tubular transport proteins
- Autoimmune diseases such as Sjögren’s syndrome or lupus
- Medications and toxins damaging renal tubules
- Chronic kidney diseases
- Disorders causing electrolyte imbalances
Risk Factors
- Family history of RTA or related genetic conditions
- Autoimmune disorders
- Exposure to certain drugs or toxins
- Chronic kidney disease
Complications
- Chronic metabolic acidosis affecting multiple organ systems
- Bone demineralization and fractures
- Kidney stones and nephrocalcinosis
- Growth retardation in children
- Electrolyte imbalances such as hypokalemia or hyperkalemia
Prevention
- Genetic counseling for hereditary forms
- Early diagnosis and management of underlying causes
- Avoidance of nephrotoxic drugs
- Regular monitoring of acid-base and electrolyte balance
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Blood tests for acid-base status and electrolytes
- Urine tests measuring pH and electrolyte excretion
- Genetic testing for inherited forms
- Imaging studies to assess kidney structure and complications
Medical Treatments
- Oral bicarbonate or citrate supplements to neutralize acid
- Potassium supplements for hypokalemia
- Treatment of underlying autoimmune or metabolic conditions
- Dietary modifications to reduce acid load
Interventional & Surgical Treatments
- Rarely required, but surgical intervention may be needed for complications like nephrocalcinosis or kidney stones
Advanced Therapies
- Use of tailored therapies based on genetic findings
- Multidisciplinary care involving nephrologists, endocrinologists, and geneticists
Rehabilitation and Support
- Regular follow-up for growth and bone health in children
- Monitoring of kidney function and acid-base balance
- Nutritional counseling to support treatment
- Patient and family education for chronic management
Top Hospitals or Clinics in Korea for Renal Tubular Acidosis
- Seoul National University Hospital – Leading center for kidney metabolic disorders
- Asan Medical Center – Expertise in rare renal tubular diseases
- Samsung Medical Center – Advanced diagnostics and genetic testing
- Yonsei Severance Hospital – Comprehensive multidisciplinary kidney care
- Korea University Anam Hospital – Specialized in metabolic and hereditary kidney disorders