Overview
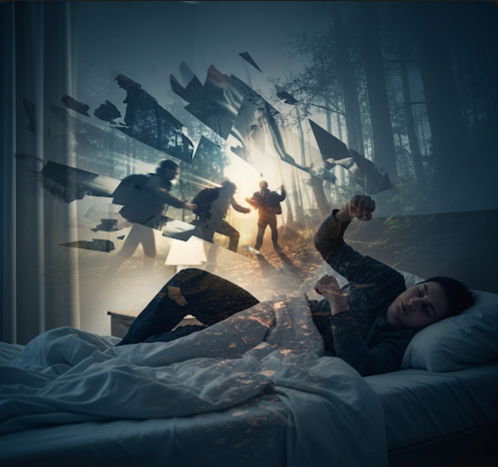
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD) is a sleep disorder characterized by the loss of normal muscle paralysis during REM sleep, leading to physical acting out of dreams. This can result in injuries to the individual or their bed partner. In Korea, sleep specialists diagnose and manage RBD with advanced tools and therapies to improve sleep safety and quality.
What is REM Sleep Behavior Disorder?
RBD involves abnormal behaviors during REM sleep when muscle atonia is typically present to prevent movement. Patients physically enact their dreams, which can include talking, shouting, punching, or kicking.
Symptoms
- Vivid, often violent dream enactment
- Movements such as punching, kicking, or flailing during sleep
- Vocalizations including shouting or yelling
- Injuries to self or bed partner
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
Causes
- Neurodegenerative disorders, especially Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia
- Medication side effects
- Brainstem lesions or injuries
- Idiopathic (unknown cause) in some cases
Risk Factors
- Older age, typically over 50 years
- Male gender
- Family history of neurodegenerative diseases
- Use of certain antidepressants or medications
Complications
- Physical injuries during sleep
- Sleep disruption leading to daytime fatigue
- Possible early marker of neurodegenerative disease
Prevention
- Safe sleeping environment to prevent injury
- Avoiding medications that worsen RBD
- Early diagnosis and treatment of underlying conditions
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves overnight polysomnography (sleep study) to detect abnormal REM sleep behaviors.
Medical Treatments
- Medications such as clonazepam or melatonin to reduce symptoms
- Adjusting or discontinuing medications that exacerbate RBD
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- No surgical treatments; management is primarily medical
Rehabilitation and Support
- Counseling on sleep safety and environment modifications
- Support for patients and caregivers
- Monitoring for progression to neurodegenerative diseases