Overview
Recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI) refers to multiple episodes of infection in the urinary tract within a specified period. It is a common problem that affects many, especially women, and can cause discomfort, frequent urination, and potential kidney complications. In Korea, urologists and infectious disease specialists offer comprehensive diagnostic and treatment strategies to manage and prevent recurrent UTIs effectively.
What is Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection?
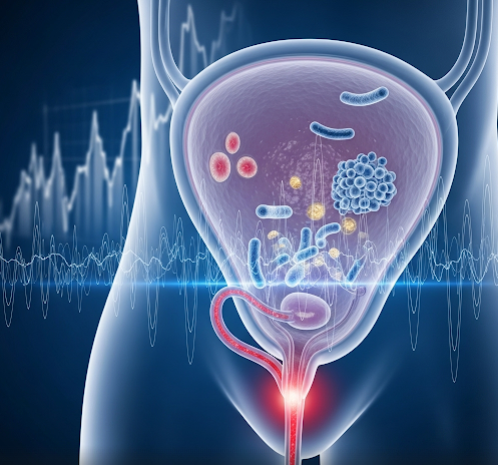
Recurrent UTI is defined as two or more infections within six months or three or more within a year. It usually involves bacterial infections affecting the bladder (cystitis), urethra (urethritis), or kidneys (pyelonephritis). Recurrence may result from reinfection or bacterial persistence.
Symptoms
- Frequent, urgent need to urinate
- Burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy, foul-smelling, or bloody urine
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Fever or chills (especially if kidneys are involved)
- Fatigue or malaise
Causes
- Bacterial infection, most commonly Escherichia coli
- Incomplete bladder emptying or urinary stasis
- Anatomical abnormalities of the urinary tract
- Sexual activity causing bacterial introduction
- Use of certain contraceptives like diaphragms
Risk Factors
- Female gender due to shorter urethra
- Postmenopausal changes leading to reduced estrogen
- Urinary catheter use
- Diabetes mellitus
- Immunosuppression
- Previous UTI history
Complications
- Kidney infections leading to pyelonephritis
- Formation of kidney or bladder stones
- Antibiotic resistance from frequent treatment
- Chronic bladder inflammation and scarring
Prevention
- Adequate hydration to flush out bacteria
- Urinating after sexual intercourse
- Proper personal hygiene
- Avoiding irritating feminine products
- Cranberry products or supplements (effectiveness varies)
- Estrogen therapy for postmenopausal women under medical advice
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes urine analysis, urine culture, and sometimes imaging studies like ultrasound or CT to detect anatomical issues.
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotic therapy based on culture and sensitivity
- Prophylactic low-dose antibiotics in selected cases
- Treatment of underlying conditions contributing to recurrence
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Surgical correction of anatomical abnormalities if identified
- Procedures to improve bladder emptying or address reflux
Rehabilitation and Support
- Patient education on prevention and lifestyle changes
- Regular follow-up to monitor for recurrence
- Support groups or counseling for chronic recurrent UTI sufferers