Overview
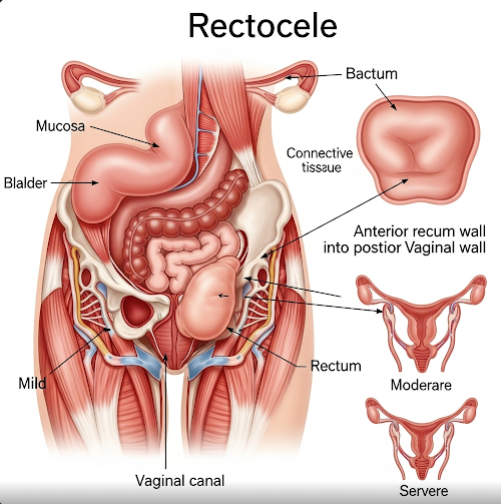
Rectocele is a condition where the rectal wall bulges into the vaginal canal due to weakness of the supporting tissues between the rectum and vagina. It commonly affects women, especially after childbirth or with aging. In Korea, gynecologists and colorectal specialists collaborate to provide accurate diagnosis and effective treatment to relieve symptoms and improve pelvic floor function.
What is Rectocele?
Rectocele occurs when the rectovaginal septum—the tissue wall between the rectum and vagina—weakens or tears, causing the rectum to bulge forward into the vaginal space. This can result in difficulty with bowel movements and vaginal discomfort.
Symptoms
- Sensation of a bulge or pressure in the vagina
- Difficulty with bowel movements or incomplete evacuation
- Constipation or need to press on the vaginal wall to pass stool
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Vaginal fullness or pain
Causes
- Childbirth-related trauma or injury to pelvic floor muscles
- Chronic constipation and straining
- Aging and loss of tissue elasticity
- Hysterectomy or pelvic surgery
- Obesity and increased abdominal pressure
Risk Factors
- Female gender, especially postmenopausal women
- Multiple vaginal deliveries
- Chronic constipation or frequent straining
- History of pelvic surgery
- Obesity and chronic cough
Complications
- Persistent constipation and discomfort
- Vaginal irritation or infections
- Sexual dysfunction
- Impact on quality of life due to pelvic pressure
Prevention
- Pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises)
- Managing constipation with fiber-rich diet and hydration
- Avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements
- Maintaining healthy body weight
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes pelvic examination, defecography, and imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI to evaluate the extent of rectocele.
Medical Treatments
- Lifestyle changes including diet modification
- Pelvic floor physical therapy
- Stool softeners and laxatives to ease bowel movements
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Surgical repair through vaginal or transanal approaches
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures
- Surgery is considered if symptoms are severe or conservative treatments fail
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative pelvic floor rehabilitation
- Counseling on bowel habits and lifestyle
- Psychological support for pelvic floor disorders