Overview
Rectal prolapse is a condition where the rectum protrudes through the anus due to weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and supporting ligaments. It can cause discomfort, bleeding, and difficulties with bowel movements. In Korea, colorectal specialists provide expert diagnosis and surgical treatments to restore normal anatomy and improve quality of life.
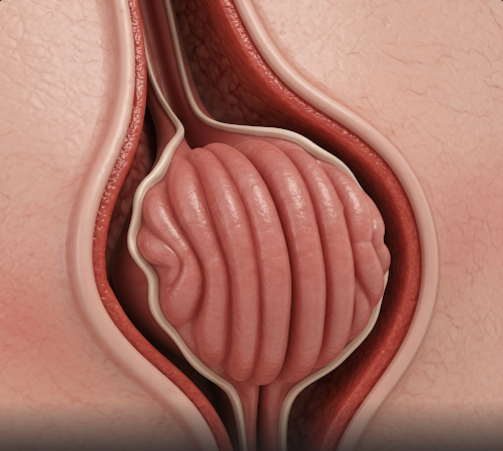
What is Rectal Prolapse?
Rectal prolapse occurs when the rectum (the final section of the large intestine) slips out of its normal position and protrudes outside the anus. This may be partial (mucosal prolapse) or complete, involving the full thickness of the rectal wall.
Symptoms
- Visible bulging or protrusion of tissue from the anus
- Sensation of incomplete bowel evacuation
- Rectal bleeding or mucus discharge
- Fecal incontinence or difficulty controlling bowel movements
- Constipation or straining during defecation
- Discomfort or pain in the anal area
Causes
- Weakening of pelvic floor muscles due to aging or childbirth
- Chronic constipation or straining
- Neurological disorders affecting pelvic nerves
- Previous pelvic surgeries or trauma
- Conditions causing increased abdominal pressure (chronic cough, obesity)
Risk Factors
- Age over 50 years
- Female gender, especially after multiple vaginal deliveries
- Chronic constipation or prolonged straining
- History of pelvic surgery or trauma
- Neurological diseases such as spinal cord injury or stroke
Complications
- Ulceration and bleeding of prolapsed tissue
- Chronic discomfort and hygiene issues
- Fecal incontinence affecting daily activities
- Recurrence after treatment if underlying causes persist
Prevention
- Managing constipation with high-fiber diet and adequate hydration
- Avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements
- Pelvic floor exercises to strengthen muscles
- Treating chronic cough or other conditions increasing abdominal pressure
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves physical examination, defecography, and colonoscopy to assess the extent of prolapse and rule out other conditions.
Medical Treatments
- Conservative management with stool softeners and pelvic floor therapy
- Lifestyle modifications to reduce straining
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Surgical repair is often required for complete prolapse
- Procedures include rectopexy (fixing rectum to sacrum), perineal procedures, or minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery
- Choice of surgery depends on patient’s age, health, and prolapse severity
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative pelvic floor rehabilitation
- Dietary counseling to prevent constipation
- Psychological support for coping with symptoms