Overview
Raynaud’s phenomenon is a vascular condition characterized by episodic narrowing of blood vessels, usually in the fingers and toes, causing color changes, numbness, and discomfort. It can be primary (idiopathic) or secondary to other diseases.
What Is Raynaud’s Phenomenon?
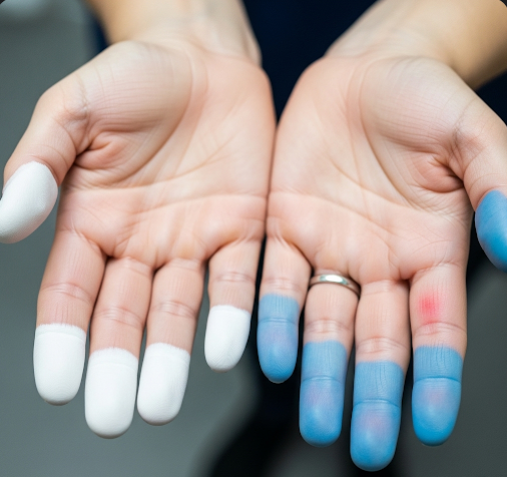
Raynaud’s phenomenon involves spasms of small blood vessels in response to cold or stress, leading to decreased blood flow. The affected areas typically turn white, then blue, and finally red upon rewarming. It may cause pain and, in severe cases, tissue damage.
Symptoms
- Episodic color changes in fingers or toes: white (pallor), blue (cyanosis), then red (hyperemia)
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Coldness and pain during attacks
- Ulcers or sores in severe cases
- Fingers or toes may feel stiff or swollen after an episode
Causes
- Primary Raynaud’s: No underlying disease, usually benign and less severe.
- Secondary Raynaud’s: Associated with autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic sclerosis, lupus), arterial diseases, or occupational exposures.
Risk Factors
- Cold climate exposure
- Female gender (more common in women)
- Family history
- Smoking
- Certain medications (beta-blockers, chemotherapy)
- Autoimmune or connective tissue diseases
Complications
- Skin ulcers or sores on fingers or toes
- Tissue necrosis in severe cases
- Infection of affected areas
- Impaired hand or foot function
Prevention
- Keeping warm and protecting extremities from cold
- Avoiding smoking
- Managing stress
- Regular monitoring if associated with systemic diseases
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers comprehensive care for Raynaud’s phenomenon including:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding cold exposure, stress management, and smoking cessation.
- Medications: Calcium channel blockers, vasodilators, and topical nitrates to improve blood flow.
- Advanced Therapies: Prostacyclin analogs, phosphodiesterase inhibitors for severe cases.
- Surgical Options: Sympathectomy in refractory cases to improve circulation.
- Management of Underlying Diseases: Rheumatology care for associated autoimmune conditions.
- Patient Education: Guidance on preventive measures and early symptom recognition.
With Korea’s multidisciplinary medical teams, patients receive personalized treatment plans aimed at reducing symptoms and preventing complications.