Overview
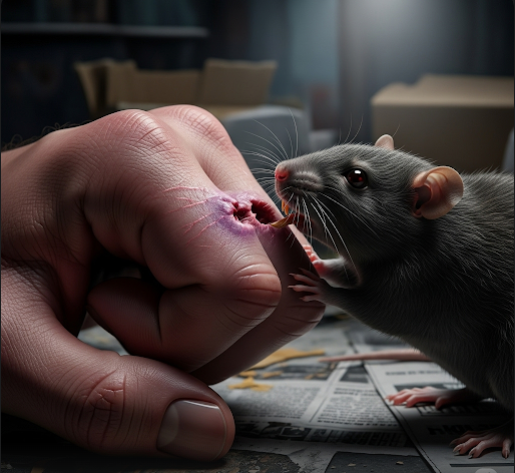
Rat-bite fever (RBF) is a bacterial infection transmitted through bites or scratches from infected rodents, mainly rats. It can also spread through contact with rodent urine or contaminated food and water. Though rare, rat-bite fever can cause serious systemic illness if untreated. In Korea, prompt diagnosis and antibiotic treatment in healthcare facilities ensure effective management and recovery.
What is Rat-Bite Fever?
Rat-bite fever is an infectious disease caused primarily by two bacteria: Streptobacillus moniliformis (more common worldwide) and Spirillum minus (more common in Asia). The bacteria enter the body through breaks in the skin caused by rodent bites or scratches, leading to systemic symptoms.
Symptoms
- Fever and chills
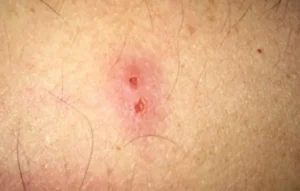
- Rash (often maculopapular or petechial)
- Joint pain and swelling (polyarthritis)
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Ulcer or wound at the bite site
Causes
The infection results from:
- Bites or scratches by infected rats or other rodents
- Handling rodents or their secretions without proper hygiene
- Ingestion of food or water contaminated with rodent excreta
Risk Factors
- Occupations or hobbies involving rodent exposure (pet shops, laboratory workers)
- Poor sanitation or living in rodent-infested areas
- Close contact with wild or domestic rodents
- Immunocompromised individuals
Complications
- Septic arthritis
- Endocarditis (infection of heart valves)
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
- Death if untreated or in severe cases
Prevention
- Avoid contact with rodents and their excreta
- Use protective gloves and clothing when handling rodents
- Maintain good hygiene and sanitation
- Control rodent populations in homes and workplaces
- Seek immediate medical attention for rodent bites or scratches
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on clinical signs, history of rodent exposure, and laboratory tests including blood cultures and PCR assays performed in Korean medical laboratories.
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics such as penicillin, doxycycline, or erythromycin
- Supportive care for symptoms
- Hospitalization in severe cases
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Drainage of abscesses or infected joints if necessary
Rehabilitation and Support
- Follow-up to ensure complete recovery
- Education on rodent exposure risks and prevention