Overview
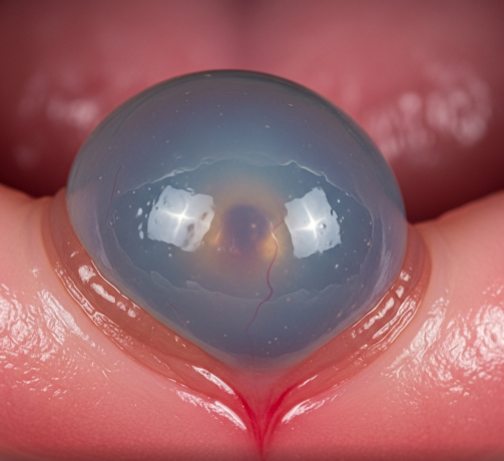
A ranula is a type of mucous cyst that forms in the floor of the mouth, usually caused by blockage or rupture of the salivary gland ducts. It appears as a painless, bluish swelling and can interfere with speaking, chewing, or swallowing if it grows large. In Korea, oral and maxillofacial specialists provide expert diagnosis and advanced treatments to effectively manage ranulas and prevent recurrence.
What is Ranula?
A ranula is a mucous retention cyst or pseudocyst arising from the sublingual salivary glands. It results when saliva leaks into surrounding tissues due to damaged or obstructed salivary ducts. Ranulas are classified as:
- Simple ranula: confined to the floor of the mouth
- Plunging ranula: extends beyond the floor of the mouth into the neck tissues
Symptoms
- Soft, painless swelling under the tongue
- Bluish, translucent appearance of the cyst
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing if large
- Discomfort or a feeling of fullness in the floor of the mouth
- Possible interference with oral hygiene
Causes
- Trauma or injury to the salivary gland ducts
- Salivary duct obstruction due to mucus plugs or inflammation
- Congenital anomalies affecting the ducts
- Chronic irritation or repeated infections
Risk Factors
- History of oral trauma or dental procedures
- Recurrent salivary gland infections
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking or alcohol use that irritates oral tissues
Complications
- Infection or abscess formation if untreated
- Recurrence after inadequate treatment
- Difficulty eating or speaking due to size or discomfort
Prevention
- Maintaining good oral hygiene
- Avoiding trauma or irritation to the floor of the mouth
- Prompt dental care for infections or injuries
- Regular dental check-ups
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean oral surgeons and ENT specialists use clinical examination, ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans to diagnose ranula and determine its extent.
Medical Treatments
- Observation for small, asymptomatic ranulas
- Needle aspiration (temporary relief, often followed by recurrence)
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Marsupialization (creating a permanent opening to drain the cyst)
- Excision of the ranula and affected salivary gland
- Minimally invasive sclerotherapy injections in select cases
Rehabilitation and Support
- Postoperative care to prevent infection
- Speech therapy if swallowing or speech are affected
- Follow-up monitoring to detect recurrence