Overview
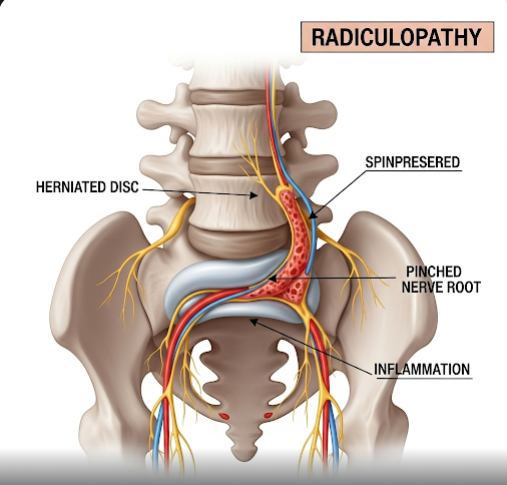
Radiculopathy is a condition caused by compression, irritation, or inflammation of a spinal nerve root, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness along the affected nerve’s pathway. It can occur in the neck (cervical), mid-back (thoracic), or lower back (lumbar) regions. The most common causes are herniated discs, spinal degeneration, and injury. In Korea, advanced spine care centers offer state-of-the-art imaging, minimally invasive treatments, and rehabilitation programs for radiculopathy, ensuring patients receive precise diagnosis and targeted therapy.
What is Radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy develops when a spinal nerve root is compressed or damaged, disrupting normal nerve signals between the spinal cord and the body. Depending on the location, it is classified as:
- Cervical radiculopathy – affects the neck, shoulders, arms, and hands.
- Thoracic radiculopathy – affects the chest and torso.
- Lumbar radiculopathy – affects the lower back, legs, and feet (sciatica is a common example).
Symptoms
- Sharp, shooting pain radiating from the spine to limbs
- Numbness or tingling in hands, arms, legs, or feet
- Muscle weakness in affected areas
- Reduced reflexes
- Pain that worsens with certain movements or positions
Causes
Radiculopathy is usually caused by conditions that put pressure on nerve roots, such as:
- Herniated or bulging discs
- Spinal stenosis (narrowing of spinal canal)
- Degenerative disc disease
- Bone spurs (osteophytes)
- Spinal injuries or fractures
- Tumors or cysts near the spine
- Inflammation from infections or autoimmune conditions
Risk Factors
- Age-related spinal wear and tear
- Repetitive heavy lifting or twisting motions
- Poor posture and weak core muscles
- Previous spine injuries
- Obesity (increases spinal load)
- Smoking (reduces disc health)
Complications
If untreated, radiculopathy can lead to:
- Permanent nerve damage
- Chronic pain syndrome
- Muscle atrophy (loss of muscle mass)
- Reduced mobility and quality of life
Prevention
- Maintaining good posture and ergonomic work habits
- Regular exercise to strengthen core and back muscles
- Avoiding excessive strain or heavy lifting
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Early treatment of spinal conditions before nerve damage progresses
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean spine specialists use physical examinations, MRI scans, CT scans, X-rays, and nerve conduction studies to confirm radiculopathy and locate the exact site of nerve compression.
Medical Treatments
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Oral or injected corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Muscle relaxants
- Physical therapy to improve flexibility and strength
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Microdiscectomy or laminectomy to relieve nerve pressure
- Endoscopic spine surgery (minimally invasive)
- Artificial disc replacement in severe degeneration
- Radiofrequency ablation for chronic pain management
Rehabilitation and Support
- Customized exercise programs
- Postural training and ergonomic adjustments
- Ongoing physiotherapy to prevent recurrence