Overview
Pleuritic chest pain is a sharp, stabbing pain in the chest that worsens with breathing, coughing, or sneezing. It is caused by inflammation or irritation of the pleura — the two thin layers of tissue that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity. While sometimes benign, pleuritic chest pain can also be a symptom of serious underlying conditions, such as pulmonary embolism, pneumonia, or autoimmune disease. Prompt evaluation is essential to determine the cause and begin appropriate treatment.
What is Pleuritic Chest Pain?
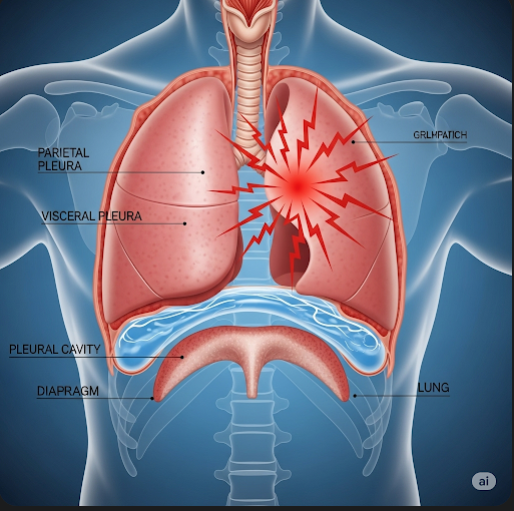
Pleuritic chest pain, also known as pleurisy, occurs when the pleural layers rub against each other due to inflammation, infection, or trauma. Under normal conditions, the pleurae slide smoothly during breathing. When inflamed, they create friction, leading to pain that typically increases during deep breaths or movement.
The pain is usually localized to one side of the chest and may radiate to the shoulder or back. It differs from other types of chest pain, such as the pressure-like pain seen in heart attacks.
Symptoms
Common features and symptoms of pleuritic chest pain include:
- Sharp, stabbing, or burning pain in the chest
- Pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or sneezing
- Shallow breathing due to fear of worsening pain
- Pain that may improve when lying on the affected side (splinting)
- Shortness of breath
- Possible fever or chills if infection is present
- Cough or sputum production in respiratory infections
- Pain localized to one side, often under the ribs
Causes
Pleuritic chest pain can result from a variety of conditions. The most common causes include:
- Viral infections – such as influenza, COVID-19, or other respiratory viruses
- Bacterial pneumonia – often accompanied by fever and productive cough
- Pulmonary embolism (PE) – a life-threatening blood clot in the lungs
- Pneumothorax – collapsed lung causing sudden sharp pain and shortness of breath
- Autoimmune diseases – like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
- Tuberculosis – in endemic areas or immunocompromised individuals
- Chest trauma or rib fractures
- Cancer – pleural mesothelioma or metastatic tumors affecting the pleura
- Pericarditis – inflammation of the heart lining may mimic pleuritic pain
- Pleural effusion – fluid buildup between pleural layers may cause irritation
Risk Factors
You may be more likely to experience pleuritic chest pain if you have:
- A history of lung disease or infections
- Recent viral illness or flu
- Pulmonary embolism risk factors (immobility, surgery, cancer, pregnancy)
- Autoimmune conditions like lupus or RA
- Smoking history
- Exposure to tuberculosis or asbestos
- Recent trauma or rib injury
- Underlying malignancy
Complications
If the underlying cause of pleuritic pain is not diagnosed and treated, complications may include:
- Respiratory failure, if caused by conditions like PE or pneumothorax
- Pleural effusion, leading to more severe breathing difficulty
- Empyema – collection of pus in the pleural space from untreated infection
- Chronic chest pain or discomfort
- Spread of infection to surrounding lung or bloodstream (sepsis)
- Reduced quality of life due to persistent pain and limited breathing
Prevention
While not all causes of pleuritic chest pain are preventable, these steps can help reduce the risk:
- Avoid respiratory infections through good hygiene and vaccinations (e.g., flu, COVID-19, pneumococcal vaccine)
- Avoid smoking and exposure to air pollutants
- Manage autoimmune disorders with appropriate medications
- Prevent blood clots through regular movement during long travel or after surgery
- Use protective gear to avoid chest trauma
- Seek early treatment for persistent cough or fever to prevent pneumonia or complications
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers world-class care in pulmonology and internal medicine, providing fast and accurate diagnosis and effective management for pleuritic chest pain.
1. Diagnosis
- Physical examination: Detection of a pleural rub with a stethoscope
- Chest X-ray or CT scan: To detect pneumonia, effusion, tumors, or pneumothorax
- D-dimer and CT angiography: To rule out pulmonary embolism
- Ultrasound: To identify pleural effusion
- Blood tests: To detect infection or autoimmune disease
- Thoracentesis: Analysis of pleural fluid, if present
- Echocardiogram: If pericarditis or cardiac causes are suspected
2. Medical Treatment
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) for pain and inflammation
- Antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia or pleuritis
- Antivirals in certain cases (e.g., influenza)
- Anticoagulants for pulmonary embolism
- Immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune causes
- Drainage of fluid or air in pleural effusion or pneumothorax
- Oxygen therapy and respiratory support if breathing is impaired
3. Hospital Care and Support
- Pulmonologists, cardiologists, and thoracic surgeons collaborate to manage serious cases
- 24/7 emergency services in top hospitals for acute chest pain evaluation
- Pain management specialists for chronic pleuritic pain
- Rehabilitation and breathing exercises for recovery
4. Leading Hospitals in Korea
Top institutions such as Asan Medical Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Severance Hospital offer:
- High-resolution imaging
- Advanced thoracic care units
- English-speaking staff and coordinated care for international patients
- Inpatient and outpatient services for lung and pleural diseases