Overview
Plasmodium infection refers to an infection caused by the Plasmodium parasite, which leads to malaria — a potentially life-threatening disease transmitted through the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito. Malaria is a global health concern, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. It affects hundreds of millions of people annually and can cause severe complications or death if left untreated. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical for successful recovery.
What is Plasmodium Infection?
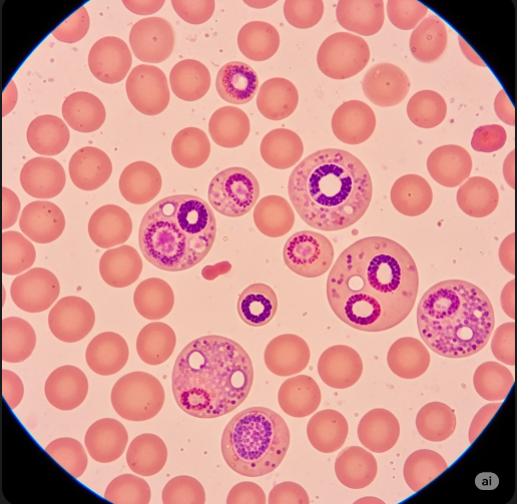
Plasmodium infection is the result of a parasitic invasion of red blood cells by Plasmodium species, leading to cyclical fevers, chills, and flu-like symptoms. The parasite is introduced into the bloodstream via a mosquito bite and travels to the liver, where it matures before re-entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells.
There are five species of Plasmodium known to infect humans:
- Plasmodium falciparum – most severe and deadly form
- Plasmodium vivax – widespread, can cause relapses
- Plasmodium ovale – less common, can also relapse
- Plasmodium malariae – milder, but can persist chronically
- Plasmodium knowlesi – a zoonotic infection found in Southeast Asia
Symptoms
Symptoms typically begin 10–15 days after the infective mosquito bite but may be delayed in some cases.
Common signs and symptoms include:
- High fever (often in cycles every 48–72 hours)
- Chills and rigors (shaking chills)
- Sweating and exhaustion after fever subsides
- Headache and muscle aches
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Anemia and jaundice due to destruction of red blood cells
- Enlarged spleen and liver
Severe cases, especially with P. falciparum, may lead to:
- Confusion or seizures (cerebral malaria)
- Difficulty breathing or pulmonary edema
- Kidney failure
- Low blood sugar
- Shock and organ failure
- Death, if untreated
Causes
Plasmodium infection is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium, transmitted through:
- Bites from infected female Anopheles mosquitoes
- Blood transfusions from infected donors
- Sharing needles or syringes
- Congenital transmission (from mother to fetus during pregnancy)
The parasite goes through several life stages in the human host and mosquito vector, making malaria a complex disease to prevent and control.
Risk Factors
Risk of infection increases with:
- Living or traveling in malaria-endemic regions, including sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- Lack of preventive measures, such as insecticide-treated bed nets or prophylactic medications
- Pregnancy, which lowers immunity
- Children under 5 years old and older adults
- Weakened immune systems
- No previous exposure or immunity (e.g., tourists or new residents in endemic areas)
Complications
If not diagnosed and treated early, Plasmodium infections can cause serious complications:
- Cerebral malaria – seizures, coma, and permanent brain damage
- Severe anemia – from destruction of red blood cells
- Respiratory distress – especially in children
- Hypoglycemia – particularly in pregnant women or those on quinine
- Multiorgan failure
- Death, particularly from P. falciparum malaria
- Relapse (in P. vivax or P. ovale) due to dormant liver stages (hypnozoites)
Prevention
Malaria prevention strategies focus on avoiding mosquito bites and chemoprophylaxis:
- Use of insect repellent (DEET-based)
- Wearing long sleeves and pants in mosquito-prone areas
- Sleeping under insecticide-treated bed nets
- Indoor residual spraying in high-risk areas
- Preventive antimalarial medications (before, during, and after travel):
- Atovaquone-proguanil
- Doxycycline
- Mefloquine
- Prompt treatment of infections to prevent further transmission
- Vaccination: RTS,S/AS01 (Mosquirix), the first malaria vaccine, is available in select countries for children
Treatment Options in Korea
While malaria is rare in South Korea, P. vivax malaria has been reported near the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), and the country has excellent capacity for early diagnosis, effective treatment, and international care for travelers or returning residents with malaria.
1. Diagnosis
- Blood smear microscopy to identify parasite species and density
- Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) available in emergency and infectious disease clinics
- PCR tests for species confirmation in complex cases
2. Antimalarial Medications
- Chloroquine: For P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae
- Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT): First-line for P. falciparum
- Artesunate + lumefantrine
- Dihydroartemisinin + piperaquine
- Primaquine: Used to eliminate liver-stage hypnozoites of P. vivax and P. ovale (requires G6PD testing before use)
- Quinine or IV artesunate: For severe malaria, available in ICU settings
3. Hospital Care
- Inpatient treatment for severe or complicated cases
- Monitoring of vital signs, organ function, and glucose levels
- Access to pediatric and obstetric care if required
4. Travel Clinics and Prevention Services
- Travel medicine clinics in major hospitals such as Samsung Medical Center, Severance Hospital, and Seoul National University Hospital offer:
- Pre-travel counseling
- Malaria prophylaxis prescriptions
- Post-travel evaluation for fever or symptoms
- English-speaking doctors and infectious disease specialists are available for international patients