Overview
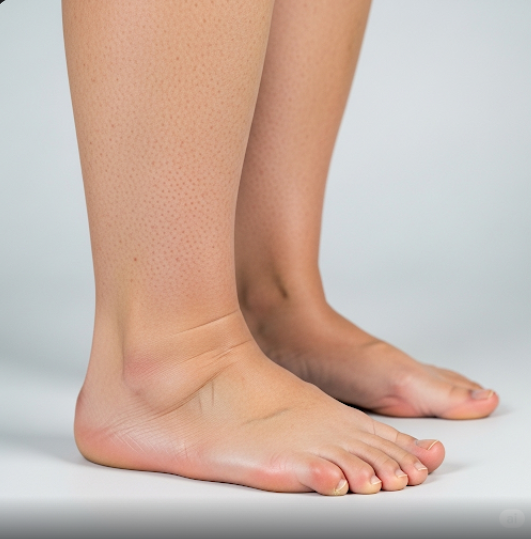
Peripheral edema refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the lower limbs—commonly the feet, ankles, and legs—resulting in noticeable swelling. It is not a disease in itself, but rather a sign of an underlying condition ranging from minor issues like prolonged standing to serious medical disorders like heart failure or kidney disease.
What is Peripheral Edema?
Peripheral edema occurs when excess fluid leaks from blood vessels into the surrounding soft tissues, particularly in the extremities. It can be classified as pitting (where pressing on the swollen area leaves a temporary dent) or non-pitting. The swelling can be mild or severe and may affect one or both sides of the body. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause is critical for effective treatment.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of peripheral edema is visible swelling, often accompanied by other signs:
- Swelling in the feet, ankles, legs, or hands
- Puffiness or a feeling of heaviness
- Tight or shiny skin over the swollen area
- Indentations left on the skin after pressure (pitting)
- Decreased flexibility or difficulty walking
- Pain, discomfort, or warmth (in some cases)
- Worsening swelling as the day progresses or after sitting/standing for long periods
Causes
Peripheral edema can result from a variety of causes, both benign and serious:
- Prolonged standing or sitting
- Pregnancy
- High salt intake
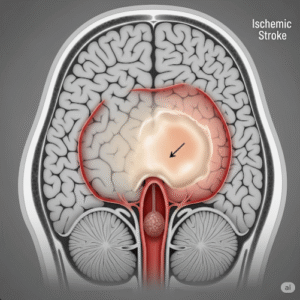
- Heart failure
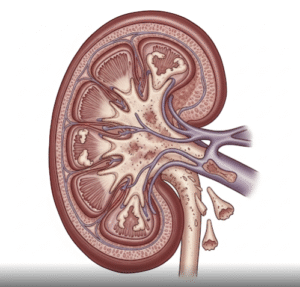
- Kidney disease or nephrotic syndrome
- Liver disease (cirrhosis)
- Chronic venous insufficiency
- Blood clots (deep vein thrombosis)
- Medications, such as calcium channel blockers, NSAIDs, steroids, or hormone therapies
- Lymphatic obstruction (lymphedema)
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are more prone to developing peripheral edema:
- Older adults
- People with cardiovascular or kidney conditions
- Those who are overweight or obese
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with sedentary lifestyles
- Patients on medications that cause fluid retention
- Long-distance travelers (due to immobility)
Complications
If not addressed, peripheral edema may lead to:
- Skin ulcers or breakdown
- Infections like cellulitis
- Decreased blood circulation
- Pain and limited mobility
- Blood clots in the deep veins
- Worsening of underlying heart, kidney, or liver conditions
Prevention
Preventing peripheral edema involves managing lifestyle factors and underlying health issues:
- Elevate legs when sitting or lying down
- Wear compression stockings if advised
- Reduce salt intake
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation
- Avoid sitting or standing for long periods without movement
- Manage chronic diseases like heart or kidney disorders
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid tight clothing around the legs
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea’s medical system provides advanced care for both the symptoms and root causes of peripheral edema through a combination of modern diagnostics, medication, and lifestyle support:
- Medical Evaluation: Korean hospitals conduct comprehensive evaluations including blood tests, urinalysis, echocardiography, kidney function tests, and Doppler ultrasound to identify the cause.
- Medication Management: Diuretics (water pills) are prescribed to help the body remove excess fluid, especially in cases related to heart, kidney, or liver disease.
- Compression Therapy: Korean vascular and rehabilitation clinics provide high-quality compression garments to improve venous return and reduce swelling.
- Lifestyle Counseling: Nutritionists and physiotherapists work with patients on diet and activity adjustments to reduce recurrence.
- Treatment of Underlying Causes:
- Heart failure management with advanced cardiology care
- Nephrology care for kidney-related fluid retention
- Liver disease management in hepatology centers
- Vascular surgery or intervention in cases of vein obstruction or varicose veins
- Integrated Care Centers: Renowned hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, and Ajou University Hospital offer coordinated, multidisciplinary treatment tailored to each patient’s needs.