Overview
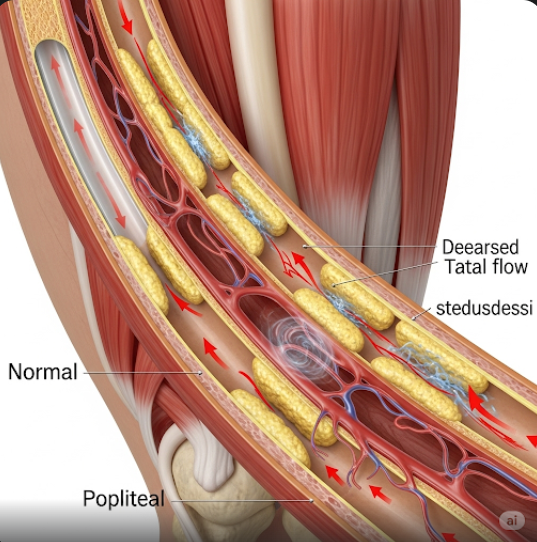
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs, especially the legs. It typically results from atherosclerosis—a buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries—which restricts oxygen-rich blood from reaching muscles and tissues. PAD can lead to pain, mobility issues, and in severe cases, tissue death or amputation if left untreated.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
Peripheral Artery Disease is a condition where the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, especially the legs and feet, become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This leads to reduced circulation, particularly during physical activity, which results in leg pain or cramping—a condition known as claudication. PAD is a sign of widespread arterial disease and may be associated with heart attack or stroke.
Symptoms
Many people with PAD have mild or no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Leg pain or cramping during walking or exercise (claudication), which goes away with rest
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Coldness in the lower leg or foot, especially compared to the other side
- Sores on toes, feet, or legs that heal slowly or not at all
- A change in leg color or shiny skin
- Weak or absent pulse in the legs or feet
- Erectile dysfunction in men (especially with diabetes)
Causes
PAD is primarily caused by atherosclerosis—plaque buildup in the arterial walls that narrows and hardens them. Other contributing causes include:
- Inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis)
- Blood clots blocking arteries
- Injury to blood vessels
- Radiation exposure
The condition may develop gradually over time, often without noticeable symptoms until it becomes advanced.
Risk Factors
Certain factors significantly increase the risk of developing PAD:
- Smoking (the most significant modifiable risk)
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol
- Aging (especially over 50)
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of cardiovascular disease
Complications
If left untreated, PAD can lead to serious complications, including:
- Critical limb ischemia: severe obstruction of blood flow leading to ulcers, gangrene, or limb amputation
- Heart attack or stroke: PAD is often a sign of widespread atherosclerosis
- Poor wound healing and increased risk of infection
- Loss of mobility or disability due to leg pain and muscle wasting
Prevention
PAD can often be prevented or its progression slowed with healthy lifestyle habits and proper management of underlying health conditions:
- Stop smoking immediately
- Maintain healthy blood sugar levels (especially in diabetics)
- Exercise regularly (walking programs are particularly effective)
- Eat a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Monitor and manage other cardiovascular conditions
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides world-class cardiovascular care, with advanced diagnostic tools and minimally invasive treatment options for Peripheral Artery Disease. The treatment approach includes:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Korean vascular specialists emphasize structured exercise therapy and smoking cessation programs supported by dietitians and rehabilitation experts.
- Medications: Drugs used to treat PAD in Korea include antiplatelet agents (aspirin, clopidogrel), statins, and medications to improve blood flow such as cilostazol.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Angioplasty and stenting: A balloon is inserted to widen narrowed arteries, sometimes followed by stent placement.
- Atherectomy: Removal of plaque from the artery using a catheter-based tool.
- Surgical Options:
- Bypass surgery: Creating a graft bypass using another blood vessel to route blood around the blocked artery.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Korean hospitals use duplex ultrasound, CT angiography, and MR angiography for early and accurate detection of PAD.
- Comprehensive Care: Multidisciplinary teams at top centers like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide integrated care, from early diagnosis to rehabilitation.