Overview
Papillary carcinoma is a form of cancer that originates in epithelial tissue and grows in small, finger-like projections. It is most commonly associated with the thyroid gland but can also occur in the breast, kidney, ovary, or bladder. Among its types, papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most prevalent and typically has a good prognosis with early detection and proper treatment. Despite its relatively slow progression, papillary carcinoma requires timely diagnosis and intervention to prevent spread or recurrence.
What is Papillary Carcinoma?
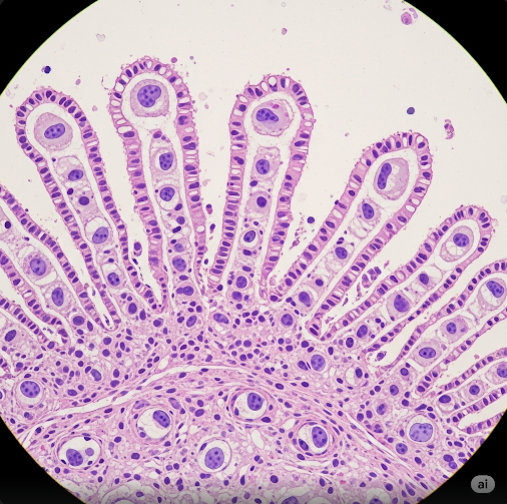
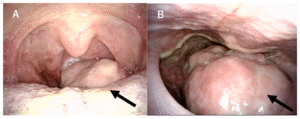
Papillary carcinoma is a malignant tumor characterized by the formation of papillae—small, finger-like protrusions lined by abnormal epithelial cells. It is considered a differentiated carcinoma, meaning the cancerous cells somewhat resemble normal cells, especially in thyroid cancer.
Common Types:
- Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (PTC) – most common type of thyroid cancer (about 80%)
- Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma – a type of kidney cancer
- Papillary Breast Carcinoma – a rare form of breast cancer
- Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma – occurs in the bladder lining
- Papillary Serous Carcinoma of the Ovary or Endometrium – aggressive form of gynecologic cancer
Each type has its own behavior and treatment protocols, but they share similar cellular architecture.
Symptoms
The symptoms of papillary carcinoma depend on the organ affected. Below are some common examples:
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma:
- Painless lump or swelling in the neck
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Difficulty swallowing
- Swollen lymph nodes
Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma:
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
- Flank pain
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
Papillary Breast Carcinoma:
- Lump in the breast
- Nipple discharge (may be bloody)
- Breast pain or swelling
Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma (bladder):
- Blood in urine
- Frequent urination
- Burning during urination
Early stages are often asymptomatic, so routine screening is important for early detection.
Causes
The exact cause of papillary carcinoma can vary, but it generally involves genetic mutations and environmental exposures:
- Radiation exposure (especially in childhood, for thyroid cancer)
- Genetic mutations (e.g., BRAF, RET/PTC rearrangements in thyroid cancer)
- Family history of cancer
- Chronic inflammation (e.g., Hashimoto’s thyroiditis for thyroid cancer)
- Smoking and chemical exposure (for bladder or kidney cancers)
- Hormonal imbalances (for breast and ovarian types)
These factors can lead to abnormal cell growth and malignant transformation.
Risk Factors
Some common risk factors for papillary carcinoma include:
- Female gender – especially for thyroid and breast types
- Age between 30–50 (for thyroid cancer)
- Previous radiation therapy to head or neck
- Family history of thyroid or other epithelial cancers
- Chronic inflammatory diseases (like thyroiditis)
- Smoking and exposure to toxins (for urinary and kidney forms)
- Obesity and metabolic disorders
Genetic predispositions (such as familial medullary thyroid carcinoma) can also elevate risk.
Complications
If not diagnosed and treated early, papillary carcinoma can lead to:
- Local invasion into nearby tissues (trachea, lymph nodes, muscle)
- Lymphatic spread, especially in thyroid and breast cancers
- Distant metastasis (lungs, bones, liver)
- Recurrence after treatment
- Complications from surgery or radiation (nerve damage, hoarseness, hypothyroidism)
- Organ dysfunction (e.g., kidney failure in renal carcinoma)
While papillary carcinoma tends to grow slowly, its complications can become serious if overlooked.
Prevention
Though not always preventable, some measures can lower the risk:
- Avoid unnecessary radiation exposure, especially to the neck
- Regular screening in high-risk individuals or those with family history
- Healthy diet and weight management
- Avoid smoking and exposure to carcinogens
- Manage chronic inflammatory conditions
- Self-examinations and awareness of bodily changes
Early detection through imaging and biopsy remains the most effective prevention against advanced-stage complications.
Treatment Option in Korea
South Korea is globally recognized for its advanced cancer care, offering cutting-edge diagnostics, personalized therapies, and minimally invasive procedures.
Diagnostic Methods:
- Ultrasound & CT/MRI for tumor localization
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) for cytology
- PET scans for metastasis detection
- Genetic testing for targeted therapy eligibility
Treatment Modalities:
- Surgery
- Thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid cancer
- Nephrectomy for kidney carcinoma
- Lumpectomy or mastectomy for breast carcinoma
- Korean hospitals like Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, and Seoul National University Hospital offer robotic and minimally invasive surgeries.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy (for thyroid cancer)
- Destroys residual thyroid tissue or metastases after surgery
- Radiation Therapy
- Used for inoperable tumors or as adjunct treatment
- Advanced precision therapies like proton therapy are available
- Targeted Therapy
- BRAF or RET inhibitors for genetic mutations
- Available under Korea’s national insurance program at top cancer centers
- Chemotherapy & Immunotherapy
- For aggressive or recurrent forms
- Korea integrates immunotherapy trials in major hospitals
- Post-treatment Monitoring
- Regular follow-up with blood markers (like thyroglobulin), imaging, and physical exams
Korea also offers international patient services, interpreter support, and affordable medical tourism packages, making it a leading destination for cancer care.