Overview
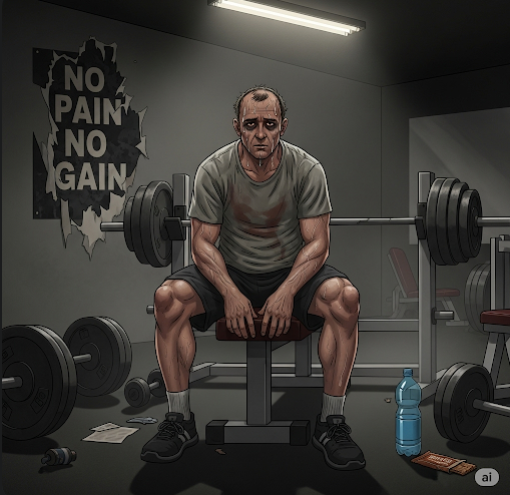
Overtraining Syndrome (OTS) is a condition that affects athletes and active individuals who engage in excessive training without adequate rest, leading to prolonged fatigue, decreased performance, and physical and psychological symptoms. In Korea, sports medicine specialists and rehabilitation centers provide expert evaluation and management to help athletes recover and prevent long-term complications.
What is Overtraining Syndrome?
Overtraining Syndrome is a state of chronic physical and mental exhaustion caused by an imbalance between intense training and insufficient recovery. Unlike normal tiredness, OTS results in a decline in athletic performance and affects multiple body systems, requiring comprehensive management.
Symptoms
Symptoms of overtraining syndrome include:
- Persistent fatigue and muscle soreness
- Decreased athletic performance despite continued training
- Mood disturbances such as irritability, depression, or anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Increased susceptibility to infections and injuries
- Loss of motivation and concentration difficulties
Causes
OTS results from repetitive intense physical activity without adequate rest and recovery. Contributing factors include:
- Excessive training volume or intensity
- Insufficient sleep and nutrition
- Psychological stress
- Inadequate periodization or training planning
Risk Factors
Risk factors for overtraining syndrome include:
- High training loads without rest periods
- Poor nutritional status
- Psychological stress or lack of social support
- Competitive athletes with intense schedules
- Inexperienced athletes increasing training too rapidly
Complications
If left unaddressed, overtraining syndrome can lead to:
- Chronic fatigue and prolonged performance decline
- Increased risk of musculoskeletal injuries
- Hormonal imbalances affecting metabolism and reproduction
- Mental health issues such as depression or anxiety
- Potential burnout and career-ending consequences for athletes
Prevention
Preventive strategies include:
- Balanced training programs with planned rest and recovery
- Adequate nutrition and hydration
- Monitoring physical and psychological signs of fatigue
- Incorporating cross-training and variation in workouts
- Regular medical and psychological evaluations
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, treatment of overtraining syndrome involves:
- Rest and recovery: Temporary cessation or significant reduction of training
- Nutritional support: Dietitians provide tailored plans to restore energy balance
- Physical therapy: To manage injuries and improve recovery
- Psychological counseling: Support for mood disturbances and stress management
- Gradual return to training: Supervised by sports medicine professionals to avoid relapse
- Multidisciplinary care: Collaboration among coaches, medical teams, nutritionists, and psychologists
Korean sports medicine clinics utilize advanced diagnostic tools and individualized rehabilitation programs to help athletes recover fully from overtraining syndrome and optimize performance.