Overview
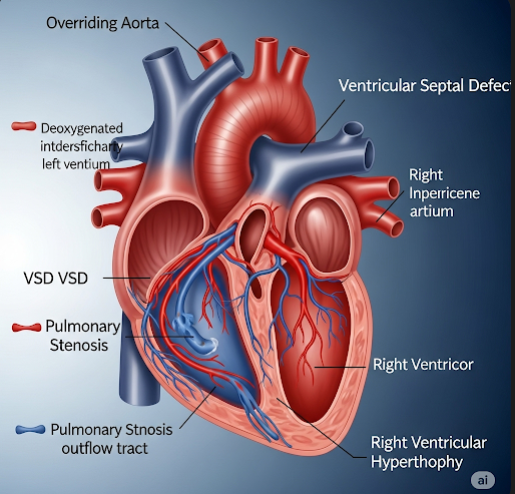
Overriding aorta is a congenital heart defect where the aorta is positioned directly above a ventricular septal defect (VSD), allowing oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle to flow into the aorta instead of only oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle. This condition is a key component of Tetralogy of Fallot, a complex heart anomaly. In Korea, advanced pediatric cardiology and cardiac surgery services offer comprehensive diagnosis and treatment to improve outcomes for affected children.
What is Overriding Aorta?
Overriding aorta occurs when the aorta, the main artery carrying blood from the heart to the body, is abnormally positioned over both the left and right ventricles, instead of just the left. This anatomical anomaly results in mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, leading to reduced oxygen supply to the body.
Symptoms
Symptoms of overriding aorta often overlap with those of Tetralogy of Fallot and may include:
- Cyanosis (bluish tint to skin, lips, and nails)
- Difficulty breathing and rapid breathing
- Poor feeding and failure to thrive in infants
- Fatigue and exercise intolerance in older children
- Heart murmur detected by a physician
Causes
Overriding aorta is caused by abnormal development of the heart during fetal life, specifically malalignment of the ventricular septum and aorta. The exact cause is often multifactorial, involving genetic and environmental factors.
Risk Factors
Risk factors include:
- Family history of congenital heart defects
- Maternal illnesses such as diabetes or rubella during pregnancy
- Genetic syndromes like DiGeorge syndrome
- Exposure to certain medications or toxins during pregnancy
Complications
If untreated, overriding aorta can lead to:
- Severe hypoxia and cyanotic spells
- Heart failure due to increased workload
- Arrhythmias and sudden cardiac events
- Delayed growth and developmental issues
Prevention
While congenital, some risk can be reduced by:
- Proper prenatal care and screening
- Avoiding harmful exposures during pregnancy
- Genetic counseling for at-risk families
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for overriding aorta is typically part of managing Tetralogy of Fallot and includes:
- Surgical repair: Corrective surgery in infancy to close the ventricular septal defect and reposition the aorta
- Medical management: Supportive care before surgery including oxygen therapy and medications
- Long-term follow-up: Regular cardiology assessments and imaging to monitor heart function
- Advanced cardiac care centers: Korean hospitals provide pediatric cardiac surgery with experienced multidisciplinary teams and advanced technology
Korea’s pediatric cardiology centers offer state-of-the-art surgical techniques and comprehensive care to improve survival and quality of life for children with overriding aorta.