Overview
Ovarian germ cell tumors are a group of rare tumors originating from the germ cells of the ovary, which are responsible for producing eggs. These tumors typically affect young women and adolescents and can be benign or malignant. In Korea, specialized oncology and gynecologic centers offer advanced diagnostic tools and multidisciplinary treatment approaches to manage ovarian germ cell tumors effectively.
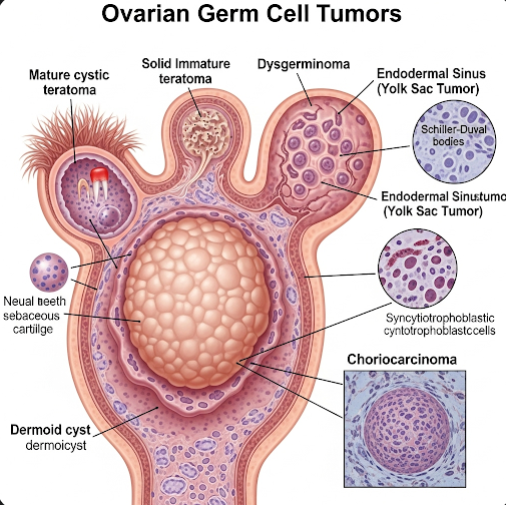
What are Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors?
Ovarian germ cell tumors arise from the cells that produce eggs within the ovary. They include various subtypes such as dysgerminomas, teratomas (including dermoid cysts), yolk sac tumors, and choriocarcinomas. These tumors often grow rapidly but respond well to chemotherapy and surgical treatment when detected early.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ovarian germ cell tumors may include:
- Abdominal or pelvic pain or swelling
- Rapidly enlarging abdominal mass
- Menstrual irregularities
- Acute abdominal pain if the tumor ruptures or causes ovarian torsion
- Nausea, vomiting, or gastrointestinal discomfort in some cases
Causes
The exact causes of ovarian germ cell tumors are not well understood. They result from abnormal development or mutation of germ cells within the ovary during fetal life or early childhood.
Risk Factors
Risk factors include:
- Young age, primarily adolescents and women under 30
- Genetic predisposition, although most cases are sporadic
- Certain chromosomal abnormalities
Complications
Complications may include:
- Tumor rupture causing acute abdominal pain and internal bleeding
- Ovarian torsion
- Spread or metastasis in malignant cases
- Impact on fertility if extensive surgery is required
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent ovarian germ cell tumors due to their developmental origin. Early diagnosis through regular medical check-ups and awareness of symptoms is important.
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, treatment of ovarian germ cell tumors involves:
- Surgical removal: Fertility-sparing surgery is preferred when possible to preserve ovarian function
- Chemotherapy: Effective for malignant tumors, with protocols such as BEP (bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin)
- Long-term follow-up: Monitoring for recurrence and managing late effects of treatment
- Fertility counseling and support: To assist patients in family planning post-treatment
- Multidisciplinary care: Coordination between gynecologic oncologists, medical oncologists, and reproductive specialists
Korean medical centers offer cutting-edge diagnostic imaging, minimally invasive surgical techniques, and personalized chemotherapy plans to optimize outcomes for patients with ovarian germ cell tumors.