Overview
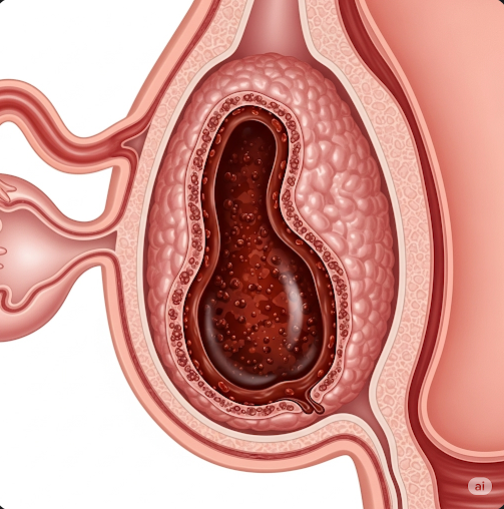
Ovarian endometrioma, commonly known as a “chocolate cyst,” is a type of ovarian cyst formed when endometrial tissue grows inside the ovary. This cyst contains thick, dark, old blood, giving it the characteristic “chocolate” appearance. It is a manifestation of endometriosis and can cause pelvic pain and fertility issues. In Korea, specialized gynecological centers offer advanced diagnostic tools and effective treatments to manage ovarian endometriomas and improve quality of life.
What is Ovarian Endometrioma (Chocolate Cyst)?
An ovarian endometrioma is a cyst formed by ectopic endometrial tissue trapped within the ovary. This tissue responds to hormonal cycles, causing bleeding and cyst formation filled with old blood. Endometriomas are a hallmark of ovarian endometriosis and are associated with chronic pelvic inflammation.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ovarian endometriomas may include:
- Chronic pelvic pain or dysmenorrhea (painful periods)
- Pain during intercourse
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Pelvic heaviness or pressure
- Occasionally, acute pain if the cyst ruptures
Causes
Ovarian endometriomas arise from the implantation of endometrial cells outside the uterus, a condition known as endometriosis. These cells implant on the ovary and form cysts through cyclical bleeding and inflammation.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for ovarian endometriomas include:
- Family history of endometriosis
- Early onset of menstruation
- Short menstrual cycles
- Higher estrogen levels
- Delayed childbirth or never having given birth
Complications
Complications from ovarian endometriomas may include:
- Chronic pelvic pain and adhesions
- Infertility due to ovarian damage or tubal involvement
- Cyst rupture leading to acute abdominal pain
- Rare risk of malignant transformation
Prevention
There is no definitive prevention for ovarian endometriomas, but early diagnosis and management of endometriosis can reduce cyst formation and complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, treatment of ovarian endometriomas includes:
- Medical therapy: Hormonal treatments such as oral contraceptives, GnRH agonists, or progestins to reduce cyst size and pain
- Surgical management: Laparoscopic cystectomy to remove the cyst while preserving ovarian tissue, especially in women desiring fertility
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): For women facing infertility, options like IVF are available
- Pain management and supportive care: Multidisciplinary approaches involving pain specialists and counseling
- Regular monitoring: Ultrasound follow-ups to assess cyst size and progression
Korean gynecological centers provide comprehensive care combining the latest surgical techniques and personalized medical management to optimize outcomes for patients with ovarian endometriomas.