Overview
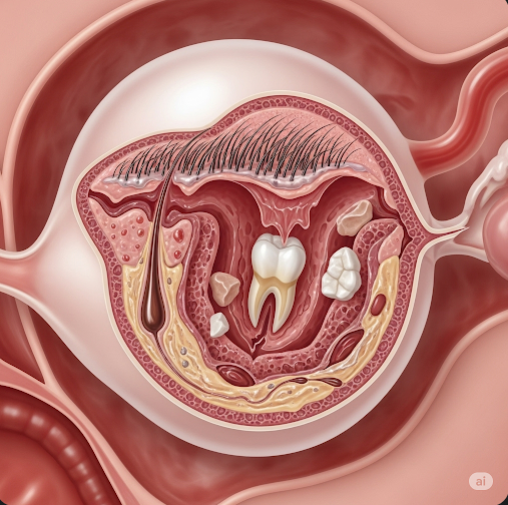
Ovarian dermoid cysts, also known as mature cystic teratomas, are common benign ovarian tumors composed of various types of tissues such as hair, skin, and fat. They typically occur in women of reproductive age and are usually slow-growing. In Korea, advanced imaging techniques and minimally invasive surgical options ensure accurate diagnosis and effective management of ovarian dermoid cysts.
What is an Ovarian Dermoid Cyst?
An ovarian dermoid cyst is a type of germ cell tumor that arises from totipotent germ cells, containing mature tissues from different germ layers. These cysts can contain hair, teeth, sebaceous material, and sometimes bone or cartilage. They are usually unilateral and benign but may cause symptoms if they grow large or undergo complications.
Symptoms
Many ovarian dermoid cysts are asymptomatic and found incidentally during imaging. When symptoms occur, they may include:
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain or discomfort
- Abdominal fullness or bloating
- Menstrual irregularities
- Acute pain if the cyst ruptures or causes ovarian torsion
- Pressure symptoms on the bladder or bowel
Causes
The exact cause of ovarian dermoid cysts is not well understood, but they originate from germ cells in the ovary during fetal development. These germ cells have the potential to differentiate into various tissue types, leading to the formation of these complex cysts.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for ovarian dermoid cysts include:
- Age between 20 and 40 years (most common)
- History of ovarian cysts
- Germ cell developmental anomalies
Complications
Possible complications include:
- Cyst rupture, causing sudden severe abdominal pain and internal irritation
- Ovarian torsion, leading to compromised blood flow and potential ovarian loss
- Rare malignant transformation into cancerous tumors
- Infection within the cyst
Prevention
There are no known prevention methods for ovarian dermoid cysts due to their developmental origin. Regular gynecologic check-ups help early detection and management.
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, treatment of ovarian dermoid cysts involves:
- Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts may be monitored with regular ultrasound exams
- Surgical removal: Laparoscopic cystectomy or oophorectomy for symptomatic, large, or complicated cysts
- Fertility preservation: Surgical techniques aim to preserve ovarian tissue in women of reproductive age
- Postoperative follow-up: Imaging to monitor for recurrence or complications
Korean gynecologic surgeons are experienced in minimally invasive techniques, offering safe and effective treatment to minimize recovery time and preserve reproductive function.