Overview
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside the ovaries. They are common in women of reproductive age and are usually benign and self-limiting. However, some cysts can cause symptoms or complications requiring medical attention. In Korea, advanced gynecological imaging and treatment options ensure accurate diagnosis and effective management of ovarian cysts.
What is Ovarian Cysts?
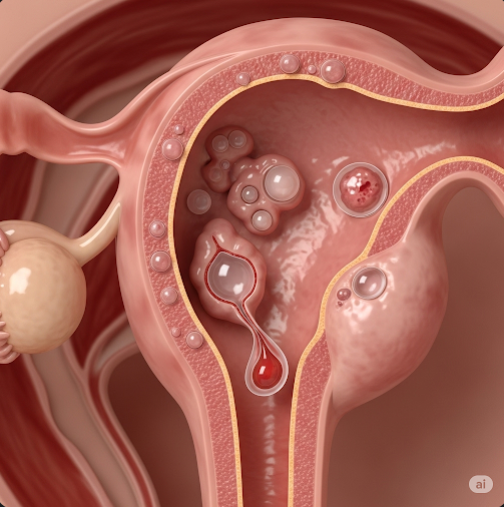
Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluid or semi-solid material that form on the ovary’s surface or within its tissue. They vary in size and type, including functional cysts related to the menstrual cycle and pathological cysts such as dermoid cysts or endometriomas. Most ovarian cysts resolve spontaneously without treatment.
Symptoms
Many ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, but when symptoms occur, they may include:
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Bloating or abdominal fullness
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder
- Sudden, severe abdominal pain if a cyst ruptures or causes ovarian torsion
Causes
Ovarian cysts develop due to various reasons, including:
- Hormonal imbalances affecting ovulation
- Functional cyst formation during the menstrual cycle
- Endometriosis causing endometriomas
- Benign or malignant tumors
- Pregnancy-related cysts such as corpus luteum cysts
Risk Factors
Risk factors for ovarian cysts include:
- Age, especially during reproductive years
- Hormonal therapy or fertility treatments
- History of ovarian cysts or endometriosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Pregnancy
Complications
Complications can arise if cysts:
- Rupture, causing severe pain and internal bleeding
- Cause ovarian torsion, cutting off blood supply to the ovary
- Grow large enough to press on nearby organs
- Are malignant (rare)
Prevention
While ovarian cysts cannot always be prevented, risk can be minimized by:
- Regular gynecological check-ups and pelvic ultrasounds
- Managing underlying conditions like PCOS or endometriosis
- Being aware of symptoms and seeking timely medical care
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for ovarian cysts in Korea depends on the cyst type, size, symptoms, and patient’s age and fertility goals:
- Observation: Many functional cysts resolve on their own and require monitoring only
- Medications: Hormonal contraceptives may be prescribed to regulate cycles and prevent new cysts
- Surgical treatment: Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery to remove persistent, large, or suspicious cysts
- Fertility preservation: Careful surgical planning to preserve ovarian function in reproductive-aged women
- Regular follow-up: Imaging and clinical assessment to monitor cyst resolution or recurrence
Korean gynecological centers use high-resolution ultrasound and expert surgical teams to provide safe, effective, and patient-centered care for ovarian cyst management.