Overview
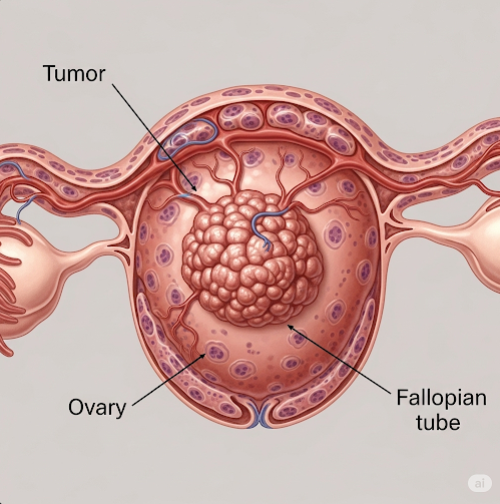
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor that originates in the ovaries, the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and hormones. It is one of the most serious gynecologic cancers due to often late diagnosis and aggressive progression. In Korea, advances in screening, surgical techniques, and chemotherapy have improved survival rates and quality of life for ovarian cancer patients.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer refers to a group of cancers that arise from different cell types within the ovary, including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. The most common type is epithelial ovarian cancer. This cancer can spread within the pelvis and abdomen and, if untreated, metastasize to distant organs.
Symptoms
Early-stage ovarian cancer often causes no or vague symptoms, but common signs include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
- Urinary urgency or frequency
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Fatigue
Causes
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown, but it is linked to genetic mutations and other factors affecting cell growth and division in ovarian tissue.
Risk Factors
Risk factors include:
- Family history of ovarian or breast cancer
- Inherited mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes
- Age over 50 years
- Endometriosis
- Never having been pregnant
- Hormone replacement therapy
Complications
Complications from ovarian cancer may include:
- Spread of cancer to other organs (metastasis)
- Bowel obstruction
- Ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdomen)
- Cachexia (severe weight loss and muscle wasting)
- Impact on fertility and hormonal balance
Prevention
While ovarian cancer cannot be completely prevented, risk reduction strategies include:
- Genetic counseling and testing for high-risk individuals
- Use of oral contraceptives, which have been shown to reduce risk
- Regular gynecologic check-ups and awareness of symptoms
- Prophylactic surgery in very high-risk cases
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for ovarian cancer in Korea involves a multidisciplinary approach:
- Surgery: Removal of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and affected tissues
- Chemotherapy: Platinum-based chemotherapy is standard, often combined with targeted therapies
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy: Emerging options for specific cancer types and genetic profiles
- Genetic testing and counseling: To guide personalized treatment and family risk assessment
- Supportive care: Pain management, nutritional support, and psychological counseling
Korean cancer centers offer advanced diagnostic imaging, minimally invasive surgery, and access to clinical trials, ensuring comprehensive and state-of-the-art care for ovarian cancer patients.