Overview
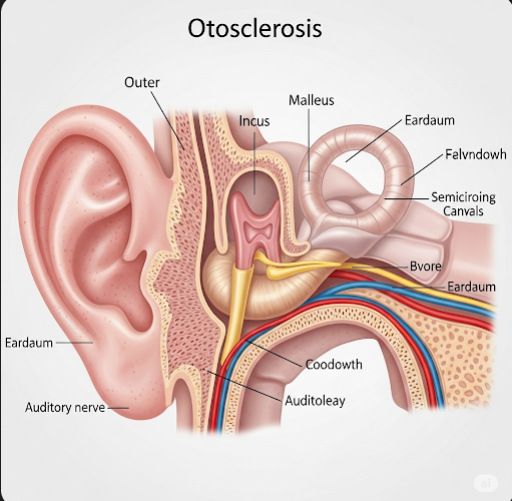
Otosclerosis is a common cause of progressive hearing loss due to abnormal bone remodeling in the middle ear, particularly affecting the stapes bone. This condition leads to stiffness of the stapes, impairing sound transmission to the inner ear. In Korea, otosclerosis is diagnosed through audiological and imaging tests, and effective treatments such as surgery and hearing aids are widely available to restore hearing.
What is Otosclerosis?
Otosclerosis is a disorder characterized by abnormal bone growth in the otic capsule of the middle ear. The disease primarily involves the stapes bone, which becomes fixed due to excessive bone deposition, preventing it from vibrating properly. This fixation leads to conductive hearing loss and, in some cases, sensorineural hearing loss if the inner ear is affected.
Symptoms
Symptoms of otosclerosis include:
- Gradual, progressive hearing loss, usually starting in one ear and often affecting both ears over time
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ear)
- Difficulty hearing low-pitched sounds
- Balance problems in rare cases
Causes
The exact cause of otosclerosis is unknown, but it is believed to involve genetic and environmental factors. It may be associated with viral infections (such as measles) and hormonal changes, which can influence the abnormal bone remodeling process.
Risk Factors
Risk factors include:
- Family history of otosclerosis
- Female gender, especially during pregnancy due to hormonal influences
- Age between 15 and 45 years, when the disease commonly develops
Complications
If untreated, otosclerosis can lead to:
- Progressive hearing loss impacting communication and quality of life
- Social isolation and difficulties in daily activities
- Possible development of sensorineural hearing loss in advanced cases
Prevention
There is no known prevention for otosclerosis, but early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms and preserve hearing.
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment for otosclerosis in Korea includes:
- Hearing aids: To amplify sound and improve hearing in mild to moderate cases
- Surgical treatment (stapedectomy or stapedotomy): Replacement or removal of the immobilized stapes bone to restore sound conduction
- Regular audiological monitoring: To track hearing changes and adjust treatment as needed
- Patient counseling and support: To help patients adapt to hearing loss and treatment options
Korean ENT specialists are skilled in advanced microsurgical techniques and provide comprehensive audiological services, ensuring effective management of otosclerosis and improved patient outcomes.