Overview
Otorrhea refers to the abnormal discharge or drainage from the external ear canal or middle ear. It can be a symptom of various underlying conditions such as infections, trauma, or chronic ear diseases. In Korea, otorrhea is commonly evaluated by ENT specialists using modern diagnostic tools, and treatments are tailored based on the underlying cause to prevent complications and restore ear health.
What is Otorrhea?
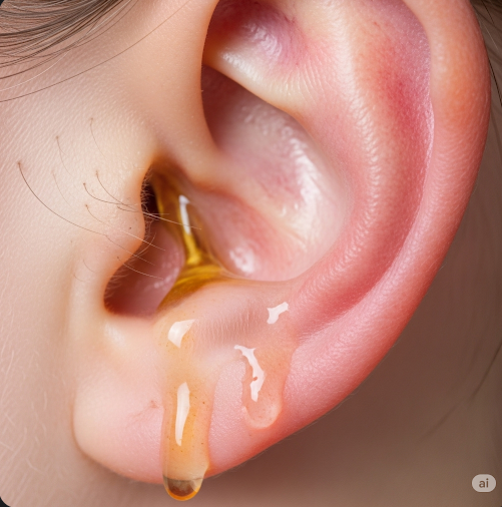
Otorrhea is the medical term for any fluid—such as pus, blood, or clear fluid—that drains from the ear. It may originate from the external ear canal or the middle ear, often indicating inflammation or infection. The discharge’s color, consistency, and odor help determine the underlying cause.
Symptoms
Symptoms associated with otorrhea include:
- Ear discharge that can be watery, purulent (pus-like), bloody, or foul-smelling
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Hearing loss or muffled hearing
- Itching or irritation in the ear
- Possible fever if infection is present
- Sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear
Causes
Common causes of otorrhea include:
- Acute or chronic otitis externa (outer ear infection)
- Otitis media with tympanic membrane perforation
- Trauma or injury to the ear canal or eardrum
- Foreign body in the ear
- Cholesteatoma (abnormal skin growth in the middle ear)
- Post-surgical drainage after ear procedures
Risk Factors
Risk factors for developing otorrhea include:
- Frequent swimming or water exposure
- Poor ear hygiene or insertion of foreign objects into the ear
- Chronic ear infections or previous ear surgery
- Immune system disorders or diabetes
- Allergies or eczema affecting the ear canal
Complications
If left untreated, otorrhea can lead to:
- Chronic ear infections and hearing loss
- Spread of infection to adjacent structures such as mastoid bone (mastoiditis)
- Tympanic membrane scarring or perforation
- Balance disturbances if the inner ear is affected
Prevention
Preventive measures for otorrhea include:
- Keeping ears dry and clean, especially after swimming
- Avoiding insertion of objects or cotton swabs into the ear canal
- Prompt treatment of ear infections
- Managing underlying skin conditions or allergies affecting the ear
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment of otorrhea in Korea depends on the underlying cause:
- Medications: Topical or systemic antibiotics, antifungals, or steroids as needed
- Ear cleaning and debridement: Performed by ENT specialists to remove debris and promote healing
- Surgical intervention: For cases with cholesteatoma or persistent perforations
- Hearing evaluation and rehabilitation: To address any associated hearing loss
- Patient education: On ear care and infection prevention
Korean ENT clinics use advanced otoscopic and imaging technologies to diagnose otorrhea causes accurately and provide personalized treatment plans ensuring effective recovery and prevention of complications.